Enzymes
advertisement

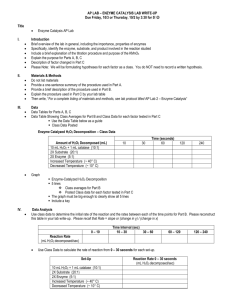
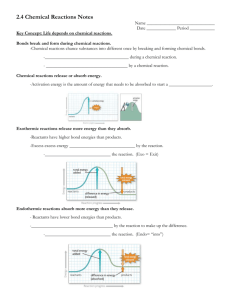
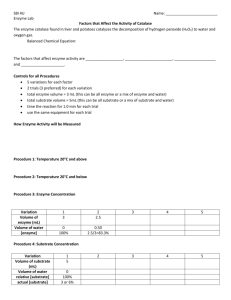
Lab: Enzymes Name______________________________ Period_________ http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab2/intro.html Enzyme Catalysis Read through the lab and answer the following questions: 1. How do enzymes catalyze reactions? ≥NEXT Key Concepts 2. What is the molecule that an enzyme acts on in the reaction? 3. What is changed in the reaction? 4. What is not changed in the reaction? Why? 5. In this reaction, what are the enzyme, substrate and product? Enzyme: Substrate: Products: 6. What happens when catalase is added to hydrogen peroxide? ≥Next Concept Enzyme Structure 7. What are enzymes? 8. What is the active site of an enzyme? ≥Next Concept Binding Specificity 9. What happens when different substrate molecules are present? ≥Next Concept Induced Fit 10. What is in induced fit? 11. What happens in an enzyme reaction when the products are released? ≥Next Concept Some Factors That Affect Enzyme Action 12. What are two important factors that affect enzymes? 13. What is denatured mean? ≥Next Concept pH and Enzyme Function 14. What type of environment does the enzyme pepsin prefer? 15. What type of environment does the enzyme Lipase prefer? 16. What happens to the active site when the pH changes? ≥Next Concept Temperature and Enzyme Function 17. What typically occurs with increased temperatures? 18. What happens to enzymes in boiling temperatures? http://bioweb.wku.edu/courses/Biol114/enzyme/enzyme1.asp Web Lab on Enzymes 1. Write the equation for the reaction that the enzyme catalase carries out? 2. Why does raising the temperature increase the rate of the reaction? 3. What can be used to STOP the reaction of catalase? Why does this work? Click on the “more” button 4. What is the active site? 5. If we start with 3 ml of H2O2 from your bathroom cabinet and add catalase. After 3 minutes we measure the amount of H2O2 remaining and find 1 ml remains. How much H2O2 was consumed in the reaction? 6. If we repeat the experiment above but found 2 ml of H2O2 remaining, would this indicate a lower or higher rate of reaction? Click on the “more” button 7. The Experimental Procedure-fill in the blanks _______________ tubes containing catalase and ________________ at different temperatures and examine the rate of enzyme activity by ________________ any remaining (unreacted substrate. This will give us an indirect measure of the substrate converted to _______________ and therefore the ________________ of reaction. 8. When you added H2O2 to the test tubes you added substrate or enzyme? 9. The four tubes were placed in what temperatures? 10. After you added catalase, wait 3 minutes and then add what? _______________ Why is this step important? 11. What reaction occurred in the test tubes? 12. Titrate using KMNO4 each of the four test tubes and fill out the table below Test Tube 1 Test Tube 2 Test Tube 3 Test Tube 4 Amount of KMNO4 Needed 13. Which tube had the highest rate of reaction? 14. What variable(s) would have caused the differences in reaction rates for each tube? 15. Application: Amylase is an enzyme in salvia that helps to break starches into sugars. An experiment with amylase and starch was set up similar to the one you did above and the following results were obtained. Instead of measuring the amount of starch remaining in the tube, scientists measured the amount of glucose produced. Amount of glucose in each tube after 3 minutes Test Tube 1 2 ml Test Tube 2 6 ml Test Tube 3 4 ml Test Tube 4 12 ml 16. Which of the tubes in the above experiment was the coldest? Which one was the warmest?