Enzymes - Glenelg High School
advertisement

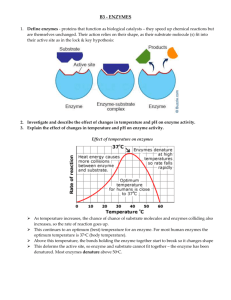
Objective: SWBAT describe the importance of enzymes by examining their roles in the human body. SAT Word: dilemma (n) a difficult or perplexing situation or problem Drill: 1. What is the monomer for proteins? 2. What is the function of a protein? 3. What is an enzyme? Key Vocabulary • Enzyme • Activation Energy • Substrate • Active Site • Catalyst Enzyme Lab Notes Enzymes What is an enzyme? • A type of protein used to speed up chemical reactions • Acts as a catalyst What is a catalyst? • An enzyme that speeds up chemical reactions without being affected • Works by lowering the activation energy for the reaction What is activation energy? • The energy needed to start a chemical reaction Why do we need enzymes? • Without them, reactions would occur so slowly that organisms would not be able to sustain life. What are some examples of enzymes? • Lactase • Catalase • Amylase • Polymerase »Do you notice a pattern? What are some examples of enzymes? • Lactase • Catalase • Amylase • Polymerase »Do you notice a pattern? What does –ase indicate? • The suffix –ase indicates an enzyme How do enzymes work? • They are very specific • They only work in certain conditions, with certain molecules • The fit with the molecules like a lock and key How do they work? Cont’d • Enzymes bind with molecules called substrates Active Site • They bind at the active site • When they bind together, it alters the substrate causing a reaction What types of things can affect the functioning of an enzyme? • Temperature • pH • Inhibitors (things that block the active site) Enzymes and Substrates SUBSTRATE ENZYME AFTER REACTION ENZYME SUBSTRATE AFTER REACTION Summary Let’s go back to the objective: SWBAT describe the importance of enzymes by examining their roles in the human body. ~Was the objective met? ~What did you learn today? Homework Finish the analysis questions from the Enzyme Lab