Phase Changes
advertisement
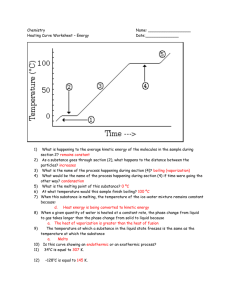
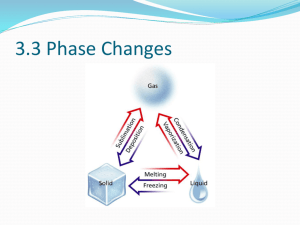
Physical Science Mr. Moss RHS When 2 states are present at the same time, we describe each as a phase. Here, we see 2 phases of water: ◦ Solid Phase ◦ Liquid Phase A Phase Change is the reversible physical change that occurs when a substance changes from one state of matter to another. There are 6 common phase changes ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Melting Freezing Vaporization Condensation Sublimation Deposition Melting Freezing NOTE: ◦ The temperature of the substance DOES NOT change during a phase change!!!! All phase changes are related to energy and temperature. Law of Conservation of Energy ◦ Neither created or destroyed. ◦ Transferred or Transformed In phase changes, energy is either absorbed or released. ◦ Endothermic – energy is absorbed. Ice melting ◦ Exothermic – energy is released. Water freezing 1g of ice absorbs 334 joules (J) of energy as it melts. This amount of energy is the Heat of Fusion for water. This is another term for the melting process. The Triple Point is where the substance exists in all 3 states. The Critical Point is where, under extreme high temps and pressure, the liquid and gaseous states are indistinguishable. Water is a molecule made up of 2 atoms of Hydrogen and 1 atom of Oxygen. The arrangement of molecules becomes less orderly as water melts. The arrangement of molecules becomes more orderly as water freezes. Endothermic process Heat energy is transformed into increased kinetic energy. Causes molecules to vibrate more rapidly. ◦ Some gain enough to overcome the attractive forces and move from the fixed locations. ◦ This is the melting point. Any energy gained after the phase change increases the average kinetic energy and the temperature rises. Exothermic Average kinetic energy (Ke) decreases causing molecules to slow down. At the freezing point, the attractive forces begin to draw the molecules into an orderly arrangement. ◦ Continues until all have been fixed. Any energy removed after the phase change is complete decreased the average kinetic energy of the molecules and the temperature decreases. Vaporization happens when a substance changes from a liquid into a gas. ◦ Endothermic ◦ Heat of vaporization Water gains 2258 J of energy when it vaporizes at 100° C. ◦ 2 vaporization processes Boiling Evaporation Takes place at the surface of a liquid Occurs at temps below the boiling point Process that changes a substance from a liquid to a gas at temps below the boiling point. In a closed container: ◦ Water vapor collects above the liquid ◦ Pressure caused by molecules colliding with container is called vapor pressure. Pressure increases as temp increases. As you apply heat energy, temperature and vapor pressure increase. When vapor pressure = atmospheric pressure, the water boils. Called the boiling point. Depends on Atmospheric Pressure ◦ Higher elevations have less atmospheric pressure Takes longer to cook food. The phase change in which a substance changes from a gas to a liquid. The water vapor transferred heat to the glass and condensed into a liquid. Sublimation is the phase change from a solid to a gas without going through the liquid phase. ◦ Endothermic ◦ Dry Ice Deposition is the phase change from a gas to a solid without going through the liquid phase. ◦ Exothermic ◦ Frost on windows