Molecular Composition of Gases
advertisement

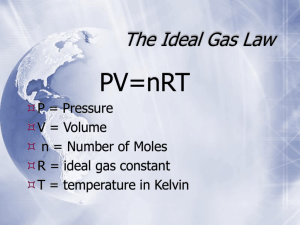
Molecular Composition of Gases The Ideal Gas Law Objectives: 1. State the ideal gas equation. 2. Derive the ideal gas constant and state its units. 3. Use the ideal gas equation to calculate the amount of gas at any condition of temperature and pressure. 4. Use the ideal gas equation to calculate the molar mass of a gas given its density. 5. Reduce the ideal gas law to Boyle’s, Charles’, GayLussac’s, or Avogadro’s Law. The Ideal Gas Law •Mathematical relationship between pressure, volume, temperature, and the number of moles of gas. Ideal Gas Law Calculate the value of R for 1 mole of gas at STP. (1 atm)( 22.4 L) L * atm 0.0821 (1 mole)( 273 K ) mol * K • The value of “R” depends on the units used for P, V, and T. • The ideal gas law can be reduced to any of the previously studied gas laws when certain variables are held constant. Sample Problems 1. A 2.07 L cylinder contains 2.88 mol of helium gas at 22oC. What is the pressure in atmospheres of the gas in the cylinder? 2. A tank of hydrogen gas has a volume of 22.9 L and holds 14.0 mol of the gas at 12oC. What is the reading on the pressure gauge in atmospheres? 3. A reaction yields 0.00856 mol of O2 gas. What volume will this occupy if it is collected at 43oC and 0.926 atm pressure? 4. What mass of ethene gas, C2H4 is contained in a 15.0 L tank that has a pressure of 4.40 atm at a temperature of 305 K? Ideal Gas Law and Molar Mass A chemist determines the mass of a sample of gas to be 3.17 g. Its volume is 942 mL at a temperature of 14oC and a pressure of 1.09 atm. What is the molar mass of the gas. 1L L atom n (0.0821 )(14 o C 273) mol K 1000 mL 1.09 atm942 mL n 0.0436 moles 3.17 g mass M 72.7 g mol moles 0.0436 mol Ideal Gas Law and Molar Mass mass Since " n" Molar mass m PV RT M mRT M PV or.... Ideal Gas Law and Density Knowing that density is mass/volume, what is the density of a sample of ammonia, if the pressure is 0.928 atm and the temperature is 63.0oC? 0.928 atm n P 0.0336 mol L L atm V RT o 0.0821 63.0 C 273 mol K 17.0305 g mol 0.572 g (0.0336 ) L L 1 mol Ideal Gas Law and Density mRT DRT M PV P MP or... D RT