Determining Geologic Ages
advertisement
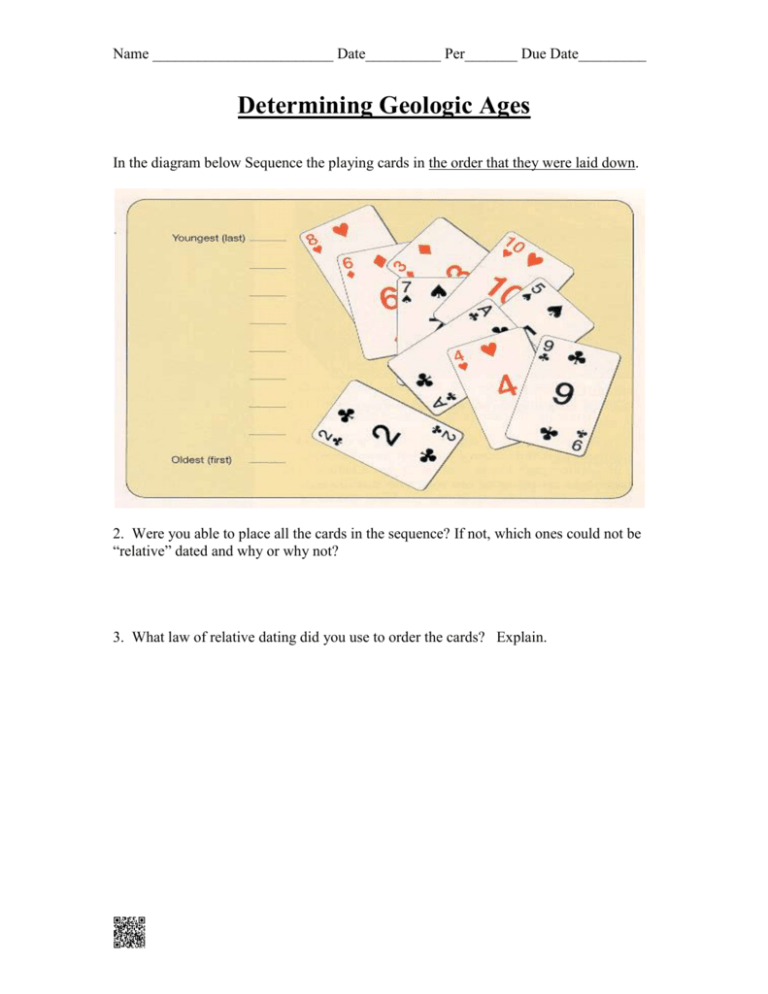
Name ________________________ Date__________ Per_______ Due Date_________ Determining Geologic Ages In the diagram below Sequence the playing cards in the order that they were laid down. 2. Were you able to place all the cards in the sequence? If not, which ones could not be “relative” dated and why or why not? 3. What law of relative dating did you use to order the cards? Explain. Name ________________________ Date__________ Per_______ Due Date_________ 4. Of the sequences of rocks, A-D and E-G, (A-D, E-G) was disturbed by crustal movements after its deposition. Circle your answer. 5. What law or principle did you apply to arrive at your answer? 6. Date the rock layers above starting with the oldest one on the left. Oldest ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ Youngest Name ________________________ Date__________ Per_______ Due Date_________ Inclusions Inclusions are pieces of one rock unit that are contained within another unit, for example, pieces of granite embedded in a shale rock sample. 7. Identify and label on the diagram the inclusions in the above diagram. 8. Of the two rocks, C and B, rock ______ is older. Why do you believe this? 9. What is the border between layer D and ABC represent? Name ________________________ Date__________ Per_______ Due Date_________ 10. Which layer in this sample is the oldest? 11. What is segment C considered geologically? 12. Fault H is _________________than the sedimentary rocks A-D. (older/younger) 13. The relative age of fault H is ________than sedimentary layer F (older/younger) 14. Did the fault occur before or after the igneous intrusion? Explain. Name ________________________ Date__________ Per_______ Due Date_________ Determining Geologic Age Extension Activity: Complete questions 15-19 using Figure 6.11 below. 15. Identify and label the unconformities indicated in the cross section. A. Between layer _________ and ___________ B. Between layer _________ and ___________ 16. Rock layer I is (OLDER/ YOUNGER) than layer J. Justify your answer with support from a principle or law. 17. The fault M is (OLDER/YOUNGER) than layer J. Justify your answer with support from a principle or law. 18. The igneous intrusion K is (OLDER/YOUNGER) than layers A and B. What two principles did you apply to determine your answer? 19. List the entire sequence of rocks from oldest to youngest on the right side of the diagram.