Epithelial Tissue - Bibb County Schools
advertisement

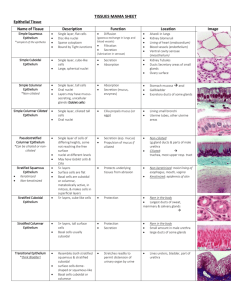
Body Tissues: Composed of specialized cells of similar structure and perform a common function Four major types: 1. Epithelial 2. _______________________ 3.Muscular 4. ________________________ ___________are typically composed of all 4 types of tissue Epithelial Tissue Cells are tightly packed __________external and internal body surfaces Also ______________and _______________substances Epithelial cells can divide to replace lost or damaged cells Cells are _______________(lack a blood supply) has a free surface and a ____________________membrane Classification of epithelial tissue Number of cell layers: ___________________epithelial tissue is one cell layer thick ___________________epithelial tissue is composed of two or more layers Shape of the cells: ________________epithelium has flattened cells Cuboidal epithelium has cube-shaped cells ________________epithelium has elongated cells Squamous Epithelium (2 kinds) 1. Simple squamous epithelium Composed of a single layer of _____________________cells Found in areas where simple _____________________occurs 2. Stratified squamous epithelium Has many cell ____________ Shape of deeper cells may be cuboidal or columnar Shape of outer cells are flattened and squamous-shaped Found in the outer portion of the __________ and in body _______________ Cuboidal Epithelium (2 kinds) 1. Simple cuboidal epithelium Single layer of ________________cells attached to a _________________membrane Found in _____________where its function is _________________ Covers the ovaries Lines most of the kidney tubules where it absorbs and secretes substances 2. Stratified cuboidal epithelium Often only has two ___________ Mostly found lining the larger ___________of certain ____________ Columnar Epithelium (2 kinds) 1.Simple columnar epithelium Cells are ____________than they are wide Modified to perform particular functions Lines digestive organs and the uterine tubes 2. Stratified columnar epithelium Not very common Located in parts of the ______________and in the male __________________ Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium Appears to have more than one layer of cells, but only has one ____________layer Each cell touches the basement ________________ Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium lines parts of the reproductive system and air passageways of the respiratory system Transitional Epithelium Changes in response to ________________ Located in_________________, the ureters, and part of the urethra Allows these organs to __________________ Connective Tissue Binds structures____________________, provides support and__________, produces blood ____________________,and stores ______________ Cells are separated by an extracellular matrix that is composed of an organic ground substance that contains the following fibers: __________________fibers __________________ fibers Reticular fibers Fibrous Connective Tissue (2 kinds) 1. Loose (areolar) connective tissue Cells of this tissue are mainly _________________ Contains many collagen and elastin fibers __________________tissue is a type of loose connective tissue in which the cells ___________and store fat 2.. Dense connective tissue Has thick bundles of collagen fibers In dense ____________________connective tissue the bundles are parallel (as in tendons and ligaments) In dense _______________ connective tissue the bundles run in different directions (in the dermis) In reticular connective tissue the cells are called reticular cells and the matrix contains only reticular fibers (also called lymphatic tissue) Cartilage Cells called _____________________are found in small chambers called lacunae Because it is avascular, it heals slowly Hyaline cartilage Most common type Contains only ______________________fibers Found in the_________, ends of long ___________and________, and in the supporting rings of the ____________ Elastic cartilage Matrix contains many elastic fibers; also contains ____________fibers; more ____________than hyaline cartilage Found in the ________________ _____________ Fibrocartilage Matrix contains strong _________________fibers Absorbs shock and reduces _______________between joints Found between the ________________and in the ___________________ Bone Extremely hard matrix composed of mineral salts deposited around collagen fibers Osteocytes (bone cells) 2 kinds of bone tissue: _________________ _________________ Blood Composed of formed elements (cells) ___________blood cells (erythrocytes) - carry oxygen ___________blood cells (leukocytes) – fight infection ___________(thrombocytes) – blood clotting Matrix is called plasma and is not formed by the tissue cells Muscular Tissue 1. Skeletal Muscle (______________________muscle) Attached to ______________of the skeleton Causes __________________of body parts Have a _________________shape and are long Muscle fibers (cells) have multiple, peripherally located ___________ Muscle fibers appear ____________due to the placement of actin and myosin filaments in the fiber 2.Smooth Muscle (___________________muscle) ______________-shaped cells Not under voluntary control (______________________) Found in the walls of hollow ________________________(organs) 3.Cardiac Muscle Found only in the walls of the ____________ _____________blood Cardiac muscle cells have________________, like skeletal muscle Is___________________, like smooth muscle Cardiac muscle cells have a single, centrally located nucleus Cardiac muscle cells are bound to one another by intercalated disks Nervous Tissue Found in the _________________and spinal cord Neurons (nervous tissue cells) conduct _______________ A neuron has three parts: 1.Dendrite – receives an __________________ 2. Cell body – contains the ________________ 3. Axon –___________________nerve impulses Neuroglia (more numerous nervous tissue cells) Support and ____________________neurons Types of neuroglia found in the brain: 1.Microglia 2.Astrocytes 3.Oligodendrocytes 4. Ependymal cells Schwann cells are neuroglia located ___________________________the brain or spinal cord Extracellular Junctions Junctions between cells help cells function as a tissue Types of cell junctions: Tight junction – plasma membrane proteins join, forming an _____________________barrier Gap junction – plasma membrane channels join, allowing ______________to pass between the two cells Adhesion junction (desmosome) – adjacent plasma membranes held together by extracellular filaments Glands Consists of one or more cells that produce and secrete a product Most are composed primarily of _____________________ Exocrine glands –______________their product onto the _____________surface or into a cavity Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete their product ________________to be transported by the _____________________ Membranes 1. Mucous membranes Line _________________walls of the organs and tubes that open to the outside of the body Consist of __________________overlying a layer of loose connective tissue Epithelium contains _____________________cells that secrete mucus 2. Serous membranes ______________________membranes line the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities Visceral membranes cover ________________organs Consist of a layer of simple squamous epithelium overlying a layer of loose connective tissue Secrete serous fluid that lubricates the membranes Pleura – serous membranes in the __________________ Parietal pleura –______________thoracic wall Visceral pleura – covers the ________________of the lungs Pericardium – covers the _________________ Peritoneum – serous membranes within the _____________________ Parietal peritoneum – lines the _________________________wall Visceral peritoneum – covers the _______________in the abdominopelvic cavity 3. Synovial membranes Line freely movable _____________cavities Composed of connective tissue Secrete synovial fluid that lubricates the ends of bones 4. Meninges Found within the _________________________cavity Composed entirely of ______________________tissue Protective ____________________for the brain and spinal cord 5.Cutaneous membrane (skin) Forms the outer covering of the ___________________ Consists of an outer portion of _________________________stratified squamous epithelium attached to a thick layer of ___________________connective tissue