tissues mama sheet
advertisement

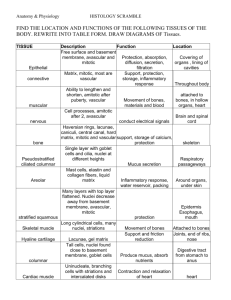
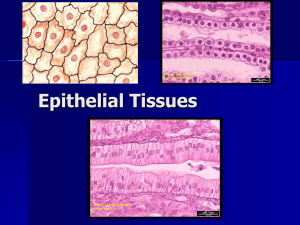
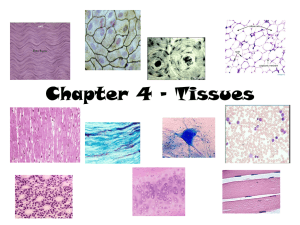
TISSUES MAMA SHEET Epithelial Tissue Name of Tissue Simple Squamous Epithelium *simplest of the epithelia Description Single layer, flat cells Disc-like nuclei Sparse cytoplasm Bound by Tight Junctions Function Diffusion (gaseous exchange in lungs and blood vessels) Filtration Secretion (lubrication in serosae) Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Single layer, cube-like cells Large, spherical nuclei Secretion Absorption Location Alveoli in lungs Kidney Glomeruli Lining of heart (endocardium) Blood vessels (endothelium) Ventral cavity serosae (mesothelium) Kidney Tubules Ducts Secretory areas of small glands Ovary surface Simple Columnar Epithelium *Non-ciliated Single layer, tall cells Oval nuclei Layers may have mucussecreting, unicellular glands (Goblet cells) Absorption Secretion (mucus, enzymes) Stomach mucosa anal Gallbladder Excretory ducts of some glands Simple Columnar Ciliated Epithelium Single layer, ciliated tall cells Oval nuclei Cilia propels mucus (or eggs) Lining small bronchi Uterine tubes, other uterine areas Single layer of cells of differing heights, some not reaching the free surface nuclei at different levels May have Goblet cells & Cilia 5+ layers Surface cells are flat Basal cells are cuboidal or columnar, metabolically active, in mitosis, & makes cells in superficial layers 5+ layers, cube-like cells Secretion (esp. mucus) Propulsion of mucus if ciliated Non-ciliated: Lg gland ducts & parts of male urethra Ciliated: trachea, most upper resp. tract Protects underlying tissues from abrasion Protection Rare in the body Largest ducts of sweat, mammary & salivary glands 5+ layers, tall surface cells Basal cells usually cuboidal Protection Secretion Rare in the body Small amount in male urethra large ducts of some glands Resembles both stratified squamous & stratified cuboidal surface cells domeshaped or squamous-like Basal cells cuboidal or columnar Stretches readily to permit distension of urinary organ by urine Lines ureters, bladder, part of urethra Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium *Can be ciliated or nonciliated Stratified Squamous Epithelium Keratinized Non-keratinized Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium Stratified Columnar Epithelium Transitional Epithelium *think Bladder! Non-keratinized: moist lining of esophagus, mouth, vagina Keratinized: epidermis of skin Image Connective Tissue Proper: Loose CT Name of Tissue Areolar CT Description Adipose CT Reticular CT Function Gel-like matrix All 3 fibers present Soft packaging body tissue Cell: fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, some WBCs Location Wraps & cushions organs Its macrophages phagocytize bacteria Big role in inflammation Holds & conveys tissue fluid Sparser matrix than Areolar Closely packed Adipocytes (fat cells) w/ nuclei pushed to the side by fat droplets Provides reserve fuel Insulates Supports & protects organs Network of reticular fibers in loose Ground Substance Fibers form soft internal skeleton supporting other cells Image Widely distributed under epithelia e.g. forms Lamina Propia mucus membranes Packages organs Surrounds capillaries Subcutaneous layer under skin Around kidneys & eyeballs In bones In abdomen & breasts Lymphoid organs: Lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen Connective Tissue Proper: Dense CT Name of Tissue Dense Regular CT Description Dense Irregular CT Elastic CT Function Mostly parallel Collagen fibers A few Elastin fibers Major cells type is the fibroblast Mostly irregularly arranged Collagen fibers Some Elastin fibers Major cells type is the fibroblast Dense CT w/ high content of Elastin fibers Location Attaches muscles to bones Withstands great tensile stress pulling in 1 direction Tendons Most ligaments Aponeuroses Withstands great tensile stress pulling in many directions Provides structural strength Dermis of skin Submucosa of Digestive tract Fibrous capsules of organs & joints Tensile strength w/ moderate elasticity Ligaments connecting adjacent vertebrae (Ligamentum Nuchae) Image