Tissues
advertisement

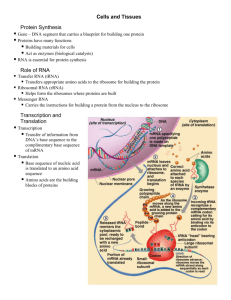
Unit 2 – Part 2 Tissues Tissues • Tissues: a group of cells with similar structure and function • Histology: the study of tissues • There are 4 primary types of tissues: – – – – Epithelium = covering Connective = support Muscle = movement Nervous = control Epithelial Tissue • Found in: – Body coverings – Body linings – Glands • Function: – Protection – Absorption – Filtration – Secretion Epithelial Tissues • Characteristics: – Cells fit closely together – Tissue always has one free surface (apical surface) – Lower surface (basal surface) bound by a basement membrane (network of fibers/connective tissue) – Regenerate easily Classification of Epithelium • Number of cell layers – Simple: one layer – Stratified: two or more layers – Pseudostratified: uneven layers Classification of Epithelium • Shape of Cells – Squamous: flattened (squamous = thin, easily removed) – Cuboidal: cube-shaped – Columnar: column-like • Combinations of these terms give us our specific Epithelium types Types of Epithelium • Simple Squamous – Description: Single layer of flat cells – Function: Usually forms membranes that allow diffusion and filtration – Present in: • Lining of body cavities • Lining of lungs and capillaries Types of Epithelium • Simple Cuboidal – Description: Single layer of cube-like cells – Function: allow secretion and absorption – Present in: • Kidney tubules • Ducts of glands • Ovary surface Types of Epithelium • Simple Columnar – Description: Single layer of tall cells • Many have cilia or microvilli • Will often have “goblet cells” – secrete mucus – Function: Absorption and Secretion – Present in: • Digestive tract, gallbladder • Ciliated: uterus, bronchi of lungs Types of Epithelium • Pseudostratified Columnar – Description: Single layer of cells with different heights • Many have cilia or microvilli • Will often have “goblet cells” – secrete mucus – Function: secretion and propulsion of mucus – Present in: • Sperm-carrying ducts • Trachea Types of Epithelium • Stratified Squamous – Description: Layers of cells, cells at the free edge are flattened – Function: Protection of underlying areas where friction is common – Present in: • Skin • Mouth • Esophagus Types of Epithelium • Stratified Cuboidal* – Rare in the body, typically 2 cell-layers thick, found in some sweat and mammary glands • Stratified Columnar* – Limited distribution in the body; surface cells are columnar, and cells underneath vary in size and shape; occurs at transition areas between 2 types of epithelium *Won’t need to identify picture Types of Epithelium • Transitional Epithelium* – Description: combination of types of cells – Function: stretching – Present in: bladder *Won’t need to identify picture Types of Epithelium • Glandular* – Gland: one or more cells that make and secrete a particular product – Two major gland types: • Endocrine gland – Ductless – Secretions are hormones • Exocrine gland – Empty through ducts onto body surfaces (skin) or into body cavities – Secretions are sweat and oil – More numerous than endocrine *Won’t need to identify picture Connective Tissue • Found in: – All areas of the body – Most abundant type of tissue! • Function: – Binds body tissues together – Supports body – Provides protection Connective Tissue • Characteristics: – Underlies epithelium – The cells are in a fiber MATRIX – there’s lots of non-living material that surrounds the living cells – Types include Bone, Cartilage, Dense Connective, Loose Connective, and Blood Types of Connective Tissue • Bone – Description: • Bone cells in cavities • Hard matrix of calcium salts • Large amount of collagen fibers – Function: used to protect and support the body Types of Connective Tissue • Cartilage: – Three types… • Hyaline cartilage – Keeps bones from rubbing together – Has abundant collagen fibers and a rubbery matrix – Most common cartilage – Entire fetal skeleton is hyaline cartilage – Found at end of long bones, rib cartilage, trachea, nose Types of Connective Tissue • Elastic Cartilage – Provides elasticity – EX: external ear, epiglottis • Fibrocartilage – Highly compressible – EX: cushion disks between vertebrae, pubic symphysis, knee joint discs Types of Connective Tissue • Dense (Fibrous) Connective – Description: Contains LOTS of collagen fibers – EX: Tendons (attach muscle to bone) and Ligaments (attach bone to bone) Types of Connective Tissue • Loose Connective – Areolar • Soft, pliable • Usually found under epithelium – Reticular • Interwoven fibers that support lots of cells • Found in lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow Types of Connective Tissue • Blood – Surrounded by fluid matrix (plasma) – Functions as the transport vehicle for materials (gases, nutrients, wastes, etc.) – Includes erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells) and Leukocytes (White Blood Cells) Muscle Tissue • Found in: Muscles! DUH! • Function: Produce movement • Characteristics: – Properties include elasticity and contractility – Three types… Muscle Tissue Types • Skeletal Muscle – Description: • Cells are striated • Cells have more than one nucleus • Cells attach to connective tissue – Function: • Voluntary control of muscles Muscle Tissue Types • Cardiac Muscle – Description: • Cells are striated • Cells have one nucleus • Cells attached to other cardiac muscles • Has Intercalated disks – Function: • Pump blood involuntary Muscle Tissue Types • Smooth Muscle – Description: • Cells are not striated • Cells have one nucleus • Cells attach to other smooth muscle cells – Function: • Surround hollow organs • Function involuntarily Nervous Tissue • Found in: Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves • Function: Send and receive impulses from other areas of the body Motor Unit! (Includes Muscle) Tissue Repair • Can happen two ways… – Regeneration: replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells – Fibrosis: repair by dense fibrous connective tissue (scar tissue) • Type of repair determined by type of tissue damaged, and by severity of the injury Tissue Repair • Tissues that regenerate easily: – Epithelial Tissue – Fibrous Connective Tissue & Bone • Tissues that regenerate poorly: – Skeletal Muscle Tissue • Tissues mainly replaced with scar tissue: – Cardiac Muscle Tissue – Nervous Tissue within brain & spinal cord