Combined Gas Law Practice
advertisement

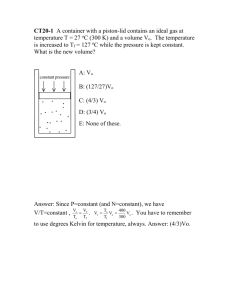
UNIT 2: GASES Scientist: ____________________ Per: _________ Date: _________ #6 Objective #1: Represent the relationships between gas temperature, volume, and pressure mathematically Combined Gas Law: Mixed Problem Set Boyle’s Law P1V1 P2V2 Charles Law V1 V2 T1 T2 Gay Lussac’s Law P1 P2 T1 T2 Combined Gas Law P1V1 P2V2 T1 T2 Absolute Temperature Conversion: K = oC + 273 Gas Law Practice Problems 1. 28 liters of oxygen gas at in a balloon is at Standard Pressure (1 atm). The gas is then forced into a 4L diving tank under high pressure. What is the pressure of the compressed oxygen? Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 2. A balloon at -73 °C with 5 L of gas is heated to 327 °C. What is the volume? Assume the pressure is constant. Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 3. An aerosol can containing 0.5 liters of nitrogen is at 1 atm and 0oC. What will the volume change to if the pressure triples to 2 atm and temperature remains constant Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 4. A Mickey Mouse balloon contains 4 liters of helium at 27oC. If the balloon is let go and rises up through the atmosphere, the temperature of the gas will cool to -173oC. If pressure were held constant, what will the volume be? Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 6. A balloon at 5 atm is placed in the sun at 77°C. After a long day, the pressure is measured at 3 atm. What must the new temperature be ( in oC) ? Assume the volume is constant. Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 7. A container with 1.2 L of gas is at 6 atm. When the gas is compressed the pressure rises to 10 atm. What is the new volume? Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 8. A container with gas at 350 kPa and 40 K is cooled to 10 K. What is the new pressure? Assume the volume is constant. Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ Page 2 of 3 9. A balloon at 50 °C with 2 L of gas is heated and the volume increases to 8 L. What is the new temperature? Assume the pressure is constant. Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 10. One mole of N2 takes up 22.4L at Standard Temperature and Pressure (1 atm and 0oC). What is the volume of 1 mole of N2 if the pressure is decreased to 0.5 atm, and the temperature remains constant? Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 11. 5 liters of nitrogen gas is at Standard Temperature and Pressure (1 atm and 0oC). What is the volume of if the temperature rises to 200oC and the pressure remains constant? Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ 12. Consider two samples of gas under the same Standard Temperature and Pressure conditions (1 atm and 0oC). Each gas begins with an equal volume: 22.4 liters of nitrogen gas and 22.4 liters of fluorine gas. As the nitrogen is heated under constant pressure to 600K, its volume expands. The fluorine gas is kept at a constant temperature, but the pressure is reduced to 0.33 atm, so it expands also. Which gas will expand more? Nitrogen Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ Fluorine Cause: _____________ is ________________ Effect: ____________ will __________________ Page 3 of 3