Ten Theories on the Fall of
advertisement
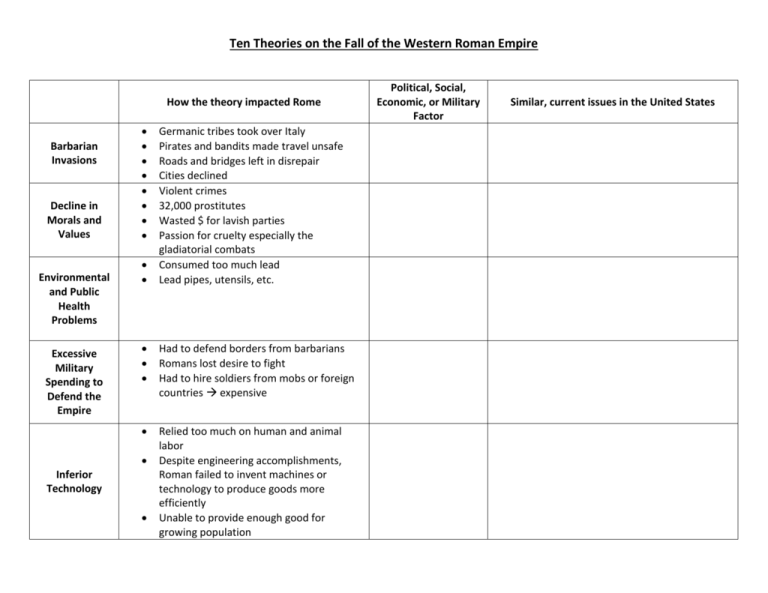
Ten Theories on the Fall of the Western Roman Empire How the theory impacted Rome Barbarian Invasions Decline in Morals and Values Environmental and Public Health Problems Excessive Military Spending to Defend the Empire Germanic tribes took over Italy Pirates and bandits made travel unsafe Roads and bridges left in disrepair Cities declined Violent crimes 32,000 prostitutes Wasted $ for lavish parties Passion for cruelty especially the gladiatorial combats Consumed too much lead Lead pipes, utensils, etc. Had to defend borders from barbarians Romans lost desire to fight Had to hire soldiers from mobs or foreign countries expensive Relied too much on human and animal labor Despite engineering accomplishments, Roman failed to invent machines or technology to produce goods more efficiently Unable to provide enough good for growing population Inferior Technology Political, Social, Economic, or Military Factor Similar, current issues in the United States Inflation Political Corruption Rise in Christianity Unemployment Urban Decay Inflation = an increase in prices Coins lost value People began to barter = traded goods for goods Salaries paid in food and clothing Taxes were collected in fruits and veggies No effective system for choosing new emperors New emperors rewarded those who chose them Eventually, throne went to highest bidder From 186 – 286 C.E., Rome had 37 different emperors – 25 of whom were removed by assassination Many followers of Christianity were pacifists (opposed war) Many qualified leaders led church instead of empire $ used to build churches and monasteries Slave-owners could produce crops cheaply Other farmers could not compete with prices so they moved to cities Not enough jobs in cities to employ everyone At one time, more than 100,000 unemployed in city of Rome Poor Romans lives in small, smelly 6+ story apartment houses The higher the room, the cheaper it was. It was also more dangerous and hotter. If could not afford apartment, they lived on the streets.