World History
advertisement

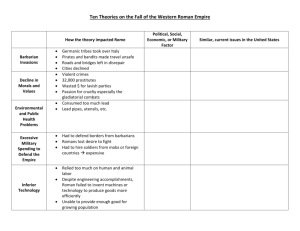
World History 3.06 The Rise and Fall of Rome The Assignment • Assignment 03.06: Please answer the following question in complete sentences using the information you learned on the previous pages. • The causes for the fall of Rome can be divided into four categories: political, military, economic and social. Using the information you have read, identify one cause in each category and explain how it contributed to the decline of the Roman Empire. The Rubric • How will this assignment be graded? • Up to 10 points for each cause and explanation. (40 points) • Up to 10 points for copying the question into your answer, writing in complete sentences, spelling, and grammar. The Link Washington State University's Rome - Click Contents and read the sections about Augustus, Imperial Rome, Calamitious Century, and The Late Empire. Click on the hyperlink, then Contents The Link The Short Answers: • The opinions that Historians have about what political (government) or military events may have started or contributed to the demise of Rome include the following: • The wealthy class becoming uninterested in politics and the army • The problem of managing the enormous size of the Roman Empire • Poor leadership by emperors, who often met untimely deaths • The success of barbarian invasions allowed by a weakened Roman army Government & Military/ Calamitous Century • An example - However, Septimius had set a precedent by seizing and retaining power using the provincial army under his control. After the death of Alexander in 235, Rome saw a half century of "barracks emperors" who were all generals and seized power in the same way Septimius Severus had done. Government & Military /Calamitous Century • An Example: • Commodus assumed the imperiate. Marcus Aurelius had been appointed by the Senate and proved to be a thoughtful and highly efficient administrator. His son, however, was slightly imbalanced. Fancying himself to be a reincarnation of Hercules, Commodus was both brutal and incompetent. He openly defied the Senate and revelled in all sorts of perversities. He was so violent and vicious, that the palace guards murdered him in 192. The Military/Crisis of the Rebublic • Marius, however, was an innovator and a maverick. He changed the fundamental make-up of his army by enlisting mainly volunteers. These volunteers were drawn from the poorest (and hence most disaffected and angry) classes, still bitter over the killings of the Gracchi. Marius held out the promise of the spoils of war and land-parcels as payment for their service (this on top of the guarantee of food and shelter for the length of their service). Something new had occurred. Poverty now pushed vast numbers of the poor into the military; these soldiers, however, owed their loyalty and gratitutde not to the state, but to their general who served as a kind of patron. This personal loyalty gave Marius, and future generals, access to civilian power that they had never had before. The Government/Imperial Rome • This was a frightening discovery in the administration of the government; now that it was apparent that military force alone produced and legitimated the emperor's rule, there was nothing to stop ambitious generals from using their armies to advance their political careers dramatically. Government/Imperial Rome • Rome acquired more of northern Africa, most of Great Britain, parts of Germany, eastern Europe around the Black Sea, as well as Mesopotami and the northern part of the Arabian peninsula. Now What? Politics/Government/Military What were the key factors? Quality of Leadership Emperors/Generals Quality of the Army Job seekers Succession-who will the next leader be No Clear Method Size of the empire Too big to manage Put your responses in your own words Helpful tips for 3.06 Economic And Social What is economic? • • • • • • Money Trade Products/production Jobs/occupations Taxes Government spending What is Social? • • • • • • • Class systems Behavior Health Entertainment Disease Crime Loyalty Read the info and write one statement for each describing the cause and explaining how it happened. Places to go for information. • FLVS intro page to 3.06 • Robert Hooker’s Rome (link off of FLVS site) The last two parts in the table of contents. “The Calamitious Century. 180-284 AD” “The Late Empire” • One of my personal favorites for the condensed version. For Example……. Economic: Inflation occurred because the Roman empire had stopped growing. Roman were not producing items to sell abroad but instead were sending the gold out of the country for luxury items. The less gold there was to use in coins meant the value of the coins was less. Merchants began