Fall of the Roman Empire: Causes & Christianity
advertisement

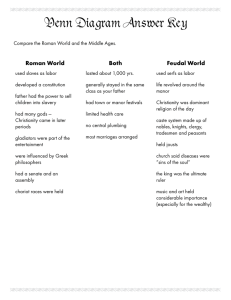
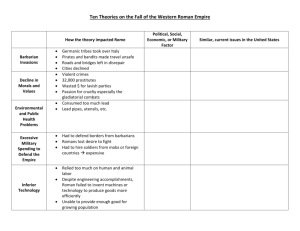
The Fall of the Roman Empire …well, sort of Roll call of the damned – 1 Corinthians - creation of the “other” - paganism; fornicators (homosexuality ?) - Roman decline - echo of Augustus emphasized Greco-Roman concept of jurisprudence - spirit and letter of the law Salvation always in peril – the Devil - Zoroastrianism Ahura Mazda – singular; all good evil exists independently - demons n’stuff - problems of perfection Paul organized early Christianity and made it appealing to a wide array of people... …but it was Roman oppression that gave Christians an added sense of identity through shared hardship I. Meanwhile, back in Rome… The Good, the Bad, the Flavian A. Dynasties 1. Julio-Claudians - Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, Nero 14-69 CE 2. Flavians 69-96 CE - Vespasian, Titus, Domitian - Equestrian, provincial 3. The Five Good Emperors Nerva - on the job training Trajan - eastern expansion (Dacia) - alimenta “welfare” 96-180 CE Hadrian - travelin’ man - Frumentarii Antoninus Marcus Aurelius - Meditations - Commodus, 180 II. Crises of the Third Century For what shall it profit a man, to gain the whole world, and forfeit his own soul? - Mark 8:36 A. Economic instability 1. Disparity 2. Decline in investment capital 3. Environmental factors - disease; pollution; soil erosion B. Political instability 1. Challenges from outside Marcommani Sassanids 2. “Enrich the Army and scorn the rest” - Septimius Severus - 235-284, 17 “Barracks Emperors” - End of the Pax Romana 192 CE 3. Decline of central control III. The Empire Restored (temporarily) Diocletian 284-305 - dominus A. Origins of serfdom 1. Social reform - tax reform B. East is East 2. Division / tetrarchy C. West Germanic Revolution 200-400 CE 1. Battle of Teutoburg Forest, 9 CE “Quinctilius Varus, give me back my legions!” 2. “Imperial” Germans - Weregeld - oaths 3. Comitatus Hermann Arminius 4. Germanic “nations” D. Diocletian’s Legacy 1. Byzantine Empire preserves Roman/Western ideals 2. Beginning of serfdom and feudal system 3. Cult of Diocletian (backfired) III. Imperial Christianity 312 A.D. - A. Constantine r. 312-337 CE 1. Persecution / conversion 2. Using one another - church financing - power of the bishops Ambrose of Milan, 390 CE Leo I & Attila the Hun, 450 CE B. Religion & politics 1. Donatists - source of priestly power 2. The Arian Heresy - those darn Greeks - Council of Nicaea 325 CE - Nicene Creed Trinity “All things visible and invisible” Rejection of rationalism C. Christianity & the Fall of the Roman Empire 1. Augustine of Hippo (354-430) - Response to Donatists and Pelargins - sack of Rome 410 CE 2. City of God ca. 411 CE city of God (Christianity) endures city of Man (Rome) is falling * Augustine argues for universal salvation… BUT, must be a member of the Church - would give Roman Church unrivaled power and legitimacy for the next 1000 years Christianity rejects rationalism, humanism in favor of mysticism and ritual