Reasons for the Fall of Rome
advertisement

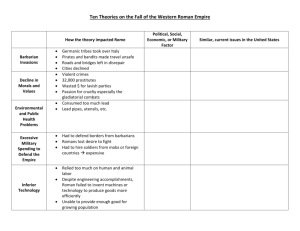
Reasons for the Fall of Rome #1 Barbarian Invasions When Roman soldiers were withdrawn from the Rhine-Danube frontier in 3rd century AD to fight in civil wars in Italy, the Roman border was left open to attack. Germanic hunters and herders from northern and central Europe began to raid and take over Roman lands in Greece and Gaul. In A.D. 476, Odovacar, the Germanic general, overthrew the last of the Roman emperors (Romulus Agustulas) and made himself ruler of Italy. #1 Barbarian Invasions From then on, the western part of the Empire was ruled by Germanic tribal chiefs. Roads and bridges were left in disrepair and many fields were left untilled. Pirates and bandits made travel unsafe. Cities declined and trade and business began to disappear. #2 Decline in Morals and Values Violent crimes made the streets of the larger cities in the Empire unsafe. There were 32,000 prostitutes in Rome during the reign of Trajan. Emperors like Nero and Caligula wasted money on lavish parties, where guests ate and drank until they became ill. Growth of the Roman passion for cruelty. Example: watching gladiatorial combats #3 Environmental and Public Health Problems Some historians believe that the leaders of Rome were killed by consuming excessive amounts of lead. Only the wealthy could afford to have lead pipes in their homes as well as lead utensils. However, this theory is challenged by the fact that the eastern part of the Empire survived long after the decline of the Western part. #4 Military Spending to Defend the Empire Spending so much money to maintain an army, left few resources for other activities such as providing public housing and maintaining the quality of public roads. Had to hire soldiers recruited from the unemployed city mobs or foreign countries. This army was unreliable and expensive. Taxes were raised frequently. This hurt the businessmen and farmers, which in turn hurt the economy. #5 Inferior Technology Even though the Romans were responsible for building marvelous roads, bridges, and aqueducts, as well as establishing the first system of medicine, they failed to invent new machines or find new technology to produce goods more efficiently. Therefore, the Romans were unable to provide important goods for their growing population. #6 Inflation Inflation= increase in prices Once the Romans stopped conquering new lands, the flow of gold decreased. However, the Romans continued to use gold to purchase luxury items. This meant that there was less gold to make coins. As the amount of gold used in coins decreased, the coins became less valuable. Merchants had no choice but to raise the prices on goods sold. # 6 Inflation Eventually, people stopped using coins and began to trade goods for goods, rather than using money. This is known as bartering. Salaries had to be paid in food and clothing. Taxes were collected in fruits and vegetables. #7 Political Corruption The Romans never created an effective system to determine how new emperors were selected. The choice of a new emperor was open to debate between the old emperor, the Senate, the emperor’s private army. Gradually the emperor’s private army gained complete control to choose the new emperor. #7 Political Corruption However, in A.D 186, the army strangled the new emperor and the practice of selling the throne to the highest bidder began. During the next 100 years, Rome had 37 different emperors, 25 of whom were assassinated. #8 Rise in Christianity Historians believe that Christianity made its followers into pacifists (those who oppose war) This made it difficult to defend Roman lands against barbarian invasions. They believe that the Church attracted qualified leaders whose talents were needed to deal with the problems that the Roman Empire faced. Believed that money was being used to build churches and monasteries, rather than being used to maintain the Empire. #9 Unemployment A farmer who had to pay workmen could not produce goods as cheaply as a farmer who used slave labor. Therefore, slave owners were able to sell their crops for lower prices. As a result, farmers could not compete with these low prices and were forced to sell or lose their farms. Thousands of these unemployed men filled the cities of the Empire, where there were not enough jobs to accommodate them. #10 Urban Decay Most Romans were not rich and had to live in small, smelly rooms in apartment homes with 6 or more stories called islands. At one time, there were 44,000 apartment houses within the city of Rome. First floor apartments were not occupied by the poor since they cost $400 per year. The upper apartments that the poor rented for $40 per year were hot, dirty, crowded, and dangerous. #10 Urban Decay Anyone who could not pay rent was forced to move out and live on the crime-infested streets. Due to this fact, the cities began to decay.