20151116075699
advertisement

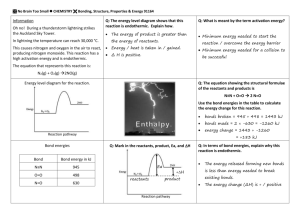
Study Guide 6.2, 6.3, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 8.3 Chapter 6 Section 2 &3 Vocabulary: Polar covalent bond, metallic bond, alloy In a polar covalent bond electrons are not shared equally which creates a partial negative charge and a partial positive charge. What determines if a molecule is polar or nonpolar? o The type of atom o The shape of the molecule Attractions between polar molecules are stronger than attractions between nonpolar molecules. A water molecule is an example of a polar molecules How do metal atoms achieve a stable electron configuration? o They lose electrons In metals valence electrons are free to move among the atom that creates a metal cation surrounded by a pool of shared electrons. How does the strength of a metallic bond vary? o Metallic bonds with alkali metals are relatively weak because they contribute only 1 valence electron. o Transition metals have more valence electrons so they create a stronger bond. o Stronger bonds have higher melting points and create harder metals. The mobility of electrons within a metal lattice explains some of the properties of metals such as conductivity and malleability. Alloys have characteristic properties of metals. What was the first important alloy? o Bronze How can scientists design alloys with specific properties? o By varying the types and amounts of elements in an alloy. Chapter 7 Section 1-3 Vocabulary: reactants, products, chemical equation, coefficients, synthesis reaction, decomposition reaction, single replacement reaction, double replacement reaction, combustion reaction Where are the reactant and products located? o Reactants are to the left of the arrow o Products are to the right of the arrom What does the law of conservation of mass state? o Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. (mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants) Be able to balance chemical equations. Be able to determine the different types of reactions. What is chemical energy? o Energy stored in chemical bonds of a substance What does a chemical reaction involve? o The breaking of chemical bonds in the reactants and the formation of chemical bonds in the products. Breaking bonds requires energy Forming bonds releases energy (can be in the form of heat and/or light) Exothermic Reaction: the release of energy (combustion is an example of an exothermic reaction) Endothermic Reaction: absorption of energy (energy of products is greater than the energy of the reactants) Chapter 8 Section 3 Vocabulary: acid, base, indicator, pH Know the characteristics of acids Know the characteristics of bases What is phenolphthalein? o An acid-base indicator Be able to determine is a substance is an acid or a base based on provided information. (i.e. characteristics, reading on a pH scale, etc.)