Applied Notes: Unit 7A—Mixtures and Solutions
advertisement

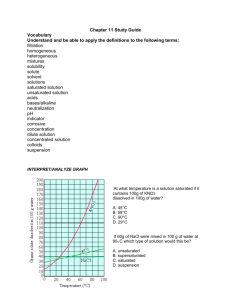
Name:___________________________________________ Period_________ Date_________________ Applied Notes: Unit 7A—Mixtures and Solutions Read each note slide to find the answers to the questions. The questions go in the order of the slides. 1. Do you remember mixtures from earlier in the semester? What is a mixture and what are the two ways we classify them? 2. What is difference between a homogeneous mixture and a heterogeneous mixture? Give an example of each using something you eat and/or drink. 3. What is a suspension? Give an example. 4. Can a suspension be separated? Yes or No? If so, how can it be done? 5. What is a colloid? Give 2 examples. Do the substances in it separate or settle-out? Yes or No 6. What is a solution? What is an example? Can a solution be separated? Yes or No 7. Fill in the table with the correct characteristics Suspension Colloid Solution Homogeneous or Heterogeneous Can be separated? Yes or No 8. What are the two parts of a solution? Define each. 9. What are two types of liquid solutions? Define each. 10. What is a concentrated solution? Name something you drink that is concentrated. 11. What is a diluted solution? Name something you drink that is diluted. 12. Complete the table with the correct response. A Concentrated solution like a extra strong cup of black coffee A Diluted solution like a cup of coffee with lots of sugar and milk Amount of SOLUTE in the solution. High or Low? Amount of SOLVENT in the solution. High or Low? 13. Solution concentration refers to the amount of what? Be sure to read the example as well. 14. Solutions are compared below. Decide which of the pairs is concentrated and which is diluted. Underline the solutions that are CONCENTRATED, circle the solution that is DILUTED . Put a star (*) next to ones that are equal. 100g of water with 5g of salt in it compared to 100g of water with 35g of salt in it 40mL of coffee with 30g of sugar in it compared to 40 mL of coffee with 0g of sugar in it 100g of water with 50g of salt in it compared to 50g of water with 25g of salt in it 10g of water with 9g of salt in it compared to 100g of water with 9g of salt in it 15. A solution that has a large amount of solute dissolved in a small amount of solvent is what: Dilute, weak, strong or concentrated?___________________________________________ 16. Do solutions only exist in the liquid phase? No! What are the 3 ways solutions can exist? 17. What is an alloy? Give an example. 18. Circle the following examples that are alloys: Copper and zinc (a penny) gold and copper oxygen and nitrogen (air) water and salt silver and copper (sterling silver) 19. What is dissolving? 20. Is a solute dissolved by a solvent or is a solvent dissolved by a solute? Circle the correct phrase. 21. The substance that is being dissolved is the what: solute, solution, solvent?_______________ 22. What does INSOLUBLE and SOLUBLE mean? 23. When oil and water are mixed, are they soluble or insoluble?________________________ 24. Circle the substances that are insoluble in water: Sugar flour grease salt alcohol vinegar fats 25. What is the term that describes the measurement of how much solute can be dissolved into a solvent? In other words, what is the term that describes how much salt can be dissolved in water at sea-level when it is 30°C?___________________________________ 26. Identify the 3 types of SOLUBILITY: 27. Identify the 3 types of solubility for each statement: The most amount of solute that can dissolve in the solvent without any solute that is not dissolved______________________________ There is space for more solute to be dissolved in the solvent_______________________ There is more solute dissolved in the solvent than is normally possible_____________________ 28. Label each drawing below as unsaturated, saturated or supersaturated? _______________ ________________ __________________ 29. Look at the solubility graph of “Solubility of KCL”. Using the terms from question #28, what is it called if the point you choose is above the line___________________________ below the line_____________________ ______or on the line___________________________ 30. To make hard candies like candy canes, Jolly Ranchers and lollipops, great amounts of sugar is dissolved in water that is heated to a high temperature. When the sugary solution is cooled, it contains more sugar in the solution than it normally can have dissolved in it at lower temperatures. This solution is now unsaturated, saturated or supersaturated? 31. Use the graph in your notes of “Temperature-Solubility Graph for Salts” to answer question below. How many grams of potassium nitrate (KNO3) will dissolve in 100mL of H2O at 40°C___________ How many grams of sodium nitrate (NaNO3) will dissolve in 100mL of H2O at 60° C___________ According to the graph, temperature affects which of the three substances the least?_________ At 40 degrees Celsius, 100g of potassium nitrate (KNO3) dissolved in 100mL of water is saturated, unsaturated or supersaturated?___________________________________ 32. What is the term that describes the amount of time required for a solvent to dissolve in a particular solute?_________________________________ 33. What are the three factors that affect the dissolving rate of a solid into a liquid? 34. Describe how temperature affects the particles in a solid and thus affects the dissolving rate: 35. How does stirring affects the particles in a solution and thus affects the dissolving rate? 36. What are 3 ways to increase the surface area of a solid? 37. Explain how increasing the surface area affects the particles in a solution and thus affects the dissolving rate? 38. Identify whether the following actions will increase (I) or decrease (D) the rate of dissolving of a substance into a solution (for instance, salt or sugar dissolving in water): Heating the substance_____ Keep the substance still_____ Tear the substance into pieces____ Stir the substance____ Crush the substance into pieces_____ Cool the substance_____ Combine substance into a larger piece_____ Cut the substance_____ Shake the solution_____ 39. The solubility of gases is different than the solubility of solids and liquids. Read the table on the solubility of gases. The complete the following: How does decreasing the temperature of a gas affect solubility?________________ How does decreasing movement (not stirring) a gas affect solubility?_____________ How does decreasing the pressure on a gas affect solubility?_______________ What are the 3 ways to increase the solubility of a gas? What has the greatest affect on the solubility of gases?____________________________ 40. In order to increase the amount of gas dissolved in a liquid, what must be done (increase or decrease) to the pressure__________________ and temperature____________________?