Part 5 study guide
advertisement

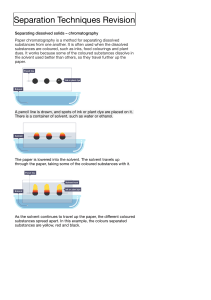
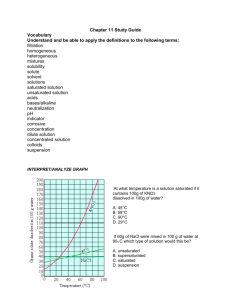
Name: KEY Date: __________ Quiz Date: _____________ Topic: Chemistry Part 5 - Acids/Bases; Properties & Reactions PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL PROPERTIES What are PHYSICAL PROPERTIES? Properties that are characteristics of a material that can be observed or measured WITHOUT destroying the material or changing it into something else. Name some examples of PHYSICAL PROPERTIES. State of matter Taste Color Shape Size Odor Texture Density Volume Luster Boiling point Conductivity Malleability Ductility Solubility pH magnetism What are CHEMICAL PROPERTIES? A chemical property tells us whether a substance has the ability to change into a new substance with different properties. Name some examples of CHEMICAL PROPERTIES. Flammability (how easily it catches on fire) Reactivity (how easily it combines with something to make something new) Combustibility (can something burn) Acidity & basicity (if a substance is an acid or a base) ACIDS AND BASES ACIDS BASES definition Compounds that increase the Compounds that increase the number number of hydrogen ions (H+) when of hydroxide ions (OH¯) when dissolved dissolved in water. in water physical properties chemical properties examples Sour taste Bitter taste Slippery Corrosive – destroy and damage other things Vinegar Orange Juice Battery Acid Lemon Juice Stomach Acid (HCI) Soda Aspirin Break down oils & greases Ammonia Soap Drain cleaner Glass cleaners Baking Soda pH 0-6 8-14 litmus test Blue litmus paper turns red Red litmus paper turns blue pH- A measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. The pH scale is from 0-14. What does pH stand for? power of Hydrogen What is neutral pH? 7 What is acidic pH? 0-6 What is basic pH? 8-14 base Weakly acidic Moderately basic 4 Weak acid 6 NEUTRALIZATION What happens when you mix an acid and a base together? When you combine an acid with a base, they cancel each other out, or neutralize each other. ACID + BASE a salt + water EXAMPLE: HCI + NaOH Hydrochloric Acid → NaCl + H₂O sodium sodium + hydroxide → chloride + water What is a salt? Salt is an Ionic compound that is formed when an acid and base neutralize each other. SOLUBILITY What is a solvent? A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances. It does the dissolving. What is a solute? The substance that is being dissolved. Why is water called The Universal Solvent? Because it is a polar molecule (has + and – ends), it dissolves a variety of substances, more than any other solvent. PHYSICAL & CHEMICAL CHANGE What is a PHYSICAL CHANGE? A change that affects one or more physical properties. Many physical changes are easy to undo. Name some examples of PHYSICAL CHANGES. o o o o o Water melting (changing state) Cutting a piece of paper (changing size) Crushing an aluminum can (changing shape) Dissolving certain substances into another substance (sugar or salt in water) Breaking glass (changing shape) What is a CHEMICAL CHANGE? A change that occurs when one or more substances are changed into entirely new substances with different properties. Chemical changes cannot be reversed using physical means. Name some examples of CHEMICAL CHANGES. Fizzing Foaming Production of heat or a precipitate Light/sparks being produced BIG color changes (like silver to red, in the case of iron rusting) Combustion Burning Rusting Tarnishing decomposing COMPOUNDS & MIXTURES ELEMENT COMPOUND MIXTURE A pure substance made of only one kind of atom A substance made of two or more different elements that are chemically combined. Two or more substances that are mixed together but not chemically combined. DEFINITION EXAMPLES Gold Sliver Carbon Chlorine Element Mixture Baking soda NaHCO₃ Rubbing alcohol (CH₃)₂CHOH Bleach NaClO Sugar C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁ Vinegar C₂H₄O₂ Compound Element Trail Mix Kool Aid Lemonade Reading Solubility Graphs