Biomes
advertisement

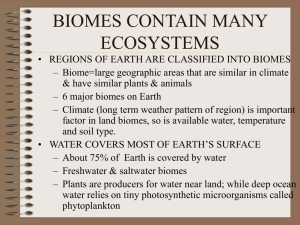
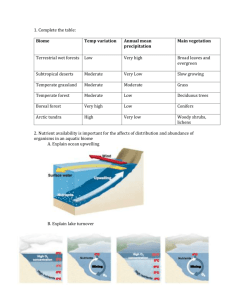
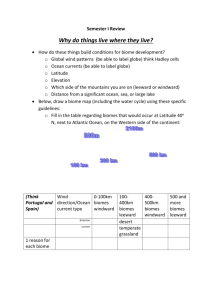
Biome Test Study Guide Test Date:____________ Biomes: A place characterized by the organisms that live there and determined by the abiotic factors of rainfall and temperature. A biome can be aquatic or terrestrial (land) and can contain one or more ecosystems. Land Biomes Temperate deciduous forest- soil is fairly rich and plants cover the forest floor - most trees are deciduous (lose their leaves in the Fall to help conserve water so they can survive winter) Coniferous/Taiga forest- conifers- trees that produce their seeds in cones and do not lose their leaves in Fall - they conserve water in the winter with the help of needlelike leaves & a waxy coating on their leaves Tropical rain forest - receives the highest yearly average rainfall - most biologically diverse (the most different types of plants and animals) - soil is wet and has poor nutrients Temperate grassland- have small, seed eating mammals, large herbivores and few trees Savanna- large herbivores live and graze on grass here, scattered clumps of trees Desert- plants grow far apart to reduce competition for water - receives the lowest average yearly rainfall Tundra- no trees, characterized by permafrost-(soil that stays frozen all the time) Permafrost prevents rain from draining which is how small plants survive Water Biomes Freshwater- characterized by a major abiotic factor→ speed at which water moves - The speed of the current determines what type of organisms live in a stream or river. tributary- each small stream or river that joins a larger stream or river estuary- an area where fresh water from streams and rivers spills into the ocean (so the fresh and salt water mix) wetland- an area of land where the water level is near or above the surface of the ground for most of the year. This area can soak up water and is plentiful in nutrients so it has many varied animals and a large amount of producers (plants). Marine- based in salty water and contain the largest organisms in the world. Phytoplankton are very small photosynthetic plant-like protists that float near the surface of the ocean. (Phytoplankton are the most abundant producers.) Zooplankton are very small animal-like protists (protozoa) that live in the ocean and eat phytoplankton. Marine biomes at the poles contain ice. Marine Zones- be able to label the zones in a picture of a marine biome Intertidal zone- area where ocean meets the land - sea grasses, periwinkle snails & birds live here Neritic zone- area where water becomes gradually deeper on the edge of the continental shelf. Seaweed, coral reefs, sea turtles, and dolphins live here. Oceanic zone- extends across the ocean waters, and down about 200m - whales, squid and animals adapted to darkness & high pressure live here. Benthic zone- the sea floor, most areas do not receive sunlight. Worms, sea urchins and bacteria live here.