Ch 34 Vocabulary - Plain Local Schools
advertisement

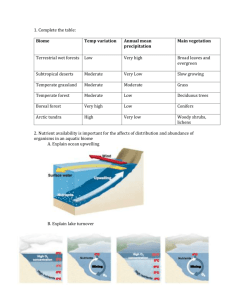
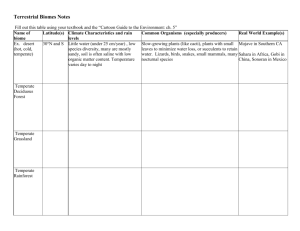
Vocabulary: Ch. 34 - The Biosphere 1. ecology2. biotic factor3. abiotic factor4. population5. community6. ecosystem7. biosphere8. habitat9. tropics10. polar zones11. temperate zones12.current13. microclimate14. biome15. tropical rain forest16. savanna17. desert18. chaparral19. temperate grassland20. temperate deciduous forest21. coniferous forest22. tundra23. permafrost 24. photic zone25. phytoplankton 26. aphotic zone 27. benthic zone 28. estuary 29. pelagic zone 30. intertidal zone 31. neritic zone 32. oceanic zone 33. zooplankton 34. hydrothermal vent Name: _________________________________ Vocabulary: Ch. 34 The Biosphere 1. ecology-scientific study of the interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment (Concept 34.1) 2. biotic factor-any living part of an environment (Concept 34.1) 3. abiotic factor- nonliving physical or chemical condition in an environment (Concept 34.1) 4. population- group of individuals of the same species living in a particular area at the same time (Concepts 1.3, 14.3, 34.1) 5. community- all the organisms living in an area (Concept 34.1) 6. ecosystem- community of living things plus the nonliving features of the environment that support them (Concepts 1.1, 34.1) 7. biosphere- all the parts of the planet that are inhabited by living things; sum of all Earth's ecosystems (Concepts 1.1, 34.1) 8. habitat- an organism's specific environment, with characteristic abiotic and biotic factors (Concept 34.1) 9. tropics- regions between 23.5° N latitude and 23.5° S latitude; warmest temperature zones on Earth (Concept 34.2) 10. polar zones-the regions north of the Arctic Circle (66.5° N) and south of the Antarctic Circle (66.5° S), that receive the smallest amount of direct sunlight year-round (Concept 34.2) 11. temperate zones- latitudes between the tropics and polar regions in each hemisphere (Concept 34.2) 12. current- riverlike flow pattern within a body of water (Concept 34.2) 13. microclimate- climate in a specific area that varies from the surrounding climate region (Concept 34.2) 14. biome- major type of terrestrial ecosystem that covers a large region of Earth (Concept 34.3) 15. tropical rain forest- type of forest near the equator that receives as much as 250 cm of rainfall yearly (Concept 34.3) 16. savanna- grassland with scattered trees; found in tropical regions of Africa, Australia, and South America (Concept 34.3) 17. desert- land area that receives less than 30 centimeters of rain per year (Concept 34.3) 18. chaparral- temperate coastal biome dominated by dense evergreen shrubs (Concept 34.3) 19. temperate grassland- biome characterized by deep, nutrient-rich soil that supports many grass species (Concept 34.3) 20. temperate deciduous forest- forest in a temperate region, characterized by trees that drop their leaves annually (Concept 34.3) 21. coniferous forest- forest populated by cone-bearing evergreen trees; mostly found in northern latitudes (Concept 34.3) 22. tundra- biome in the Arctic Circle or on high mountaintops, characterized by bitterly cold temperatures and high winds (Concept 34.3) 23. permafrost- permanently frozen subsoil (Concept 34.3) 24. photic zone- regions of a body of water where light penetrates, enabling photosynthesis (Concept 34.4) 25. phytoplankton- microscopic algae and cyanobacteria that carry out photosynthesis (Concepts 17.4, 34.4) 26. aphotic zone- deep areas of a body of water where light levels are too low to support photosynthesis (Concept 34.4) 27. benthic zone- bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms (Concept 34.4) 28. estuary- area where fresh water from streams and rivers merges with salty ocean water; productive ecosystem (Concept 34.4) 29. pelagic zone- open water above the ocean floor (Concept 34.4) 30. intertidal zone- area of shore between the high-tide and low-tide lines (Concept 34.4) 31. neritic zone- area of ocean that extends from the low-tide line out to the edge of the continental shelf (Concept 34.4) 32. oceanic zone- vast open ocean from the edge of the continental shelf outward (Concept 34.4) 33. zooplankton- microscopic animals that swim or drift near the surface of aquatic environments (Concepts 17.4, 34.4) 34. hydrothermal vent- opening in the ocean floor where hot gases and minerals escape from Earth's interior (Concept 34.4)