Biomes
advertisement

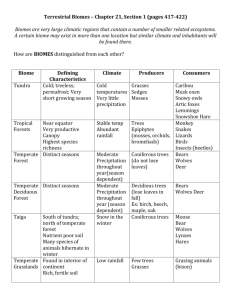
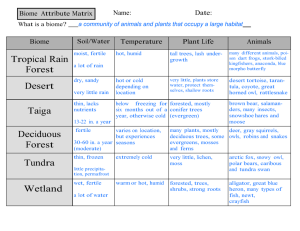
Tundra Located near the North Pole coldest and driest of all biomes long cold winters, short cool summers Has a layer of permanently frozen soil permafrost Receives very little rainfall receives very little sunlight due to the position of the Sun in the sky During the very short summer (6-10 weeks), top layer of the soil thaws just long enough to allow some plants to grow Plants are small and grow close to the ground; plants have shallow root systems – lichens, mosses, small shrubs Animals include musk ox, caribou, arctic hares, polar bear, arctic fox Taiga (coniferous forest) Largest biome in the world Has long cold winters and short, mild, wet summers. Made up of coniferous forests – trees that have cones or needles – pines, spruces and firs – evergreen trees Soil is not very fertile because there are no leaves to decompose has less diversity in plant life Animals include jays, moles, deer, moose, elk, snowshoe hare, grizzly bear, wolves Temperate Deciduous Forest Contains trees that lose their leaves each fall Has 4 seasons Lots of rain throughout the year – second most rainfall of all biomes Has very fertile soil Deciduous trees – trees that lose their leaves seasonally - such as red maple, dogwood, oak, sugar maple, beech, elm, hickory Animals include black bears, squirrels, cardinals, turkeys Grasslands found in warm and temperate areas that receive some rainfall have some of the darkest, richest soils in the world most important plants are grasses The amount of rain is not enough to grow tall trees and produce a forest, but it is enough to not form a desert. Usually flat or has gently rolling hills. Usually located between forests and deserts. Also called prairies, savannahs, plains and pampas North American animals include bison, prairie dogs, coyotes, deer. African animals - elephants, rhinoceros, hippopotamus, giraffes, lions Desert Very little rain – 10 inches or less a year Very hot during the day; cold at night Soil is dry, there is little to no surface water and evaporation is high covers a fifth of the earth’s surface There are both hot and cold deserts in the world – Antarctica is the largest desert in the world Tropical Rainforests found close to the equator rain falls all throughout the year receives the most rainfall of all biomes has the most biodiversity –more species of plants and animals than any other biome home to 50% of the world’s plant and animal species soil is low in nutrients – because of millions of years of rain and weathering, nutrients have been washed out of the soil decomposition rate is very fast – high humidity and warmth encourage rapid decay of dead plant and animal material