Semester TEST Review
advertisement
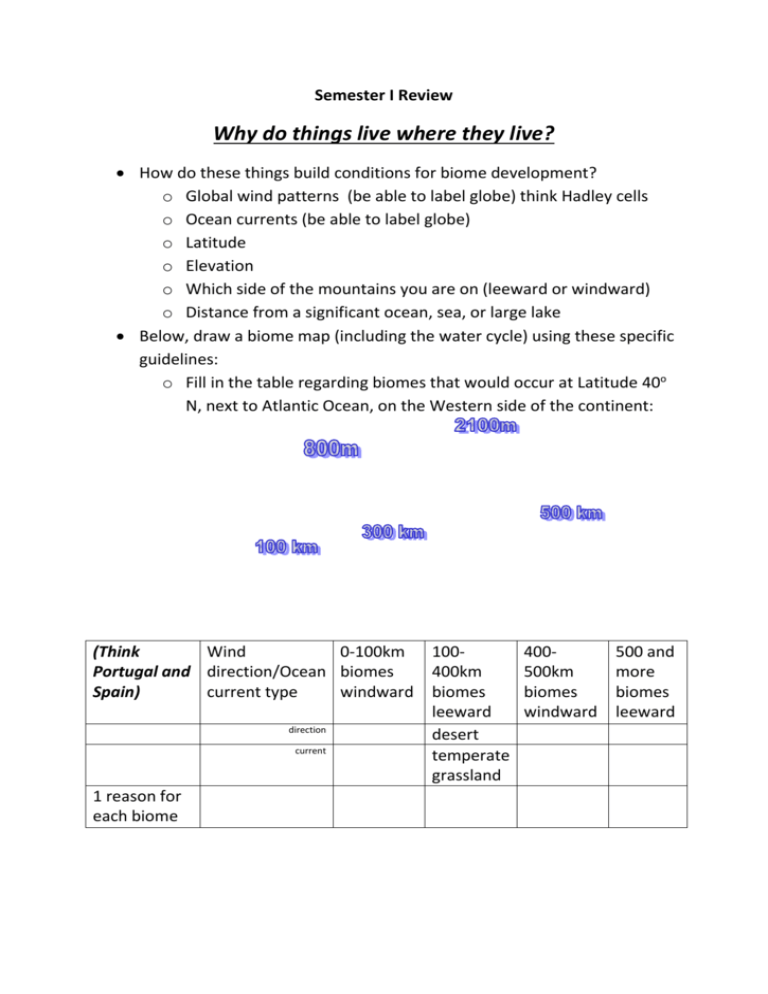
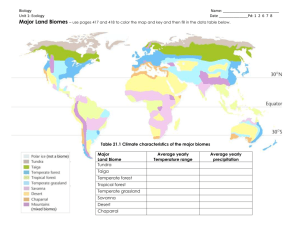
Semester I Review Why do things live where they live? How do these things build conditions for biome development? o Global wind patterns (be able to label globe) think Hadley cells o Ocean currents (be able to label globe) o Latitude o Elevation o Which side of the mountains you are on (leeward or windward) o Distance from a significant ocean, sea, or large lake Below, draw a biome map (including the water cycle) using these specific guidelines: o Fill in the table regarding biomes that would occur at Latitude 40o N, next to Atlantic Ocean, on the Western side of the continent: (Think Wind 0-100km Portugal and direction/Ocean biomes Spain) current type windward direction current 1 reason for each biome 100400km biomes leeward desert temperate grassland 400500km biomes windward 500 and more biomes leeward KNOW THESE: Primary characteristic life forms or environmental/geophysical features of the major biomes Latitude <23.5o 1. Tropical rainforest 2. Deciduous forest 30o – 65o 3. Tropical grassland 4. Temperate grassland 5. Temperate rainforest <23.5o 6. Boreal forest 50o – 65o 7. Taiga forest 30o – 65o 8. Tundra > 60o 9. Desert anywhere 10. Dry forest/shrub land 11. Alpine < 60 o >23.5o – 60o 40o – 65o Precipitation Living >300 cm rain Huge diversity 30-250 cm Trees lose leaves Other Thin soil Low diversity in winter 25 cm-75 cm Few trees Pack predators 25 cm-75 cm Tall grasses Huge herds >250 cm Largest trees Huge soil on earth production low diversity >50 cm Short Acid soils Evergreen trees >50 cm Evergreen Acid soils trees 10 cmNo trees Permafrost 100cm Short growing season <25 cm Little life Many heat and nocturnal water animals adaptations 50 cm-100 Fire resistant cm plants Mountains >25 cm anywhere on earth Short plants adapted to weather and reproduction Extremely short growing season What makes something alive? Cells The ability to reproduce without host Energy consumed to grow, repair, and reproduce Which cycle does not involve the Rock cycle (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Carbon)? Which cycle does not go into the atmosphere? In the first column below, decide whether each item is subject to Carbon, Carbon and Nitrogen, Carbon and Phosphorous, or all three cycles . For example, burial decomposition is subject to all three. Burial decomposition Combustion Consuming Excretion Respiration Volcanoes Acid rain Forming sedimentary rock Photosynthesis Coal and Fossil fuels Erosion runoff Nitrogen cycle or Nitrogen and Phosphorus cycle Ammonification Nitrification Legume/mycorrhizae Atmospheric Lightening Gas fertilizer production Decomposing bacteria Phosphorus cycle only Mining Aquatic plants’ cell membrane Mineral fertilizer production What was the Miller Urey experiment, and why was it important? What atmospheric element was missing in the primordial earth? What are abiogenesis and biogenesis? What are the basics of these three evolution theories? Radiation Punctuated equilibrium Darwinian