Study Guide for Biomes & Relationships
advertisement

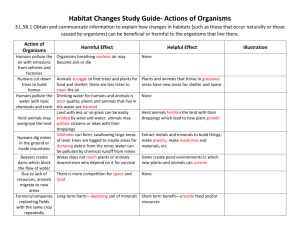
Name:____________________________________________________________________Test Date:_______________ Study Guide for Biomes & Relationships Biomes: A place characterized by the organisms that live there and determined by the abiotic factors of rainfall and temperature. A biome can be aquatic (water) or terrestrial (land) and contain one or more ecosystems. Land Biomes Temperate deciduous forest- soil is fairly rich and plants cover the forest floor - most trees are deciduous, lose their leaves in the fall to help conserve water so they can survive winter. Coniferous/Taiga forest- conifer trees that produce their seeds in cones and do not lose their leaves in fall - trees conserve water in the winter with the help of needlelike leaves and a waxy coating on their leaves Tropical rain forest - receives the highest yearly average rainfall - most biologically diverse (the most different types of plants and animals) - soil is wet and has poor nutrients Savanna- large herbivores live and graze on grass here, scattered clumps of trees Temperate grassland- have small, seed eating mammals, large herbivores and no trees Desert- plants grow far apart to reduce competition for water - receives the lowest average yearly rainfall Tundra- no trees, characterized by permafrost-(soil that stays frozen all the time. -Permafrost prevents rain from draining which is how small plants survive Freshwater- characterized by a major abiotic factor→ speed at which water moves tributary- each small stream that flows into a larger stream or river. estuary- an area where fresh water from streams and rivers spills into the ocean (so the fresh and salt water mix). wetland- an area of land where the water level is near or above the surface of the ground for most of the year. o This area can soak up water and is plentiful in nutrients so it has many varied animals and a large amount of producers (plants). Marine- based in salty water and contain the largest organisms in the world. Relationships between Organisms: Competition- when two or more individuals or populations try to use the same limited resource such as food, water, shelter, space or sunlight There are 2 major reasons for competition: 1. carrying capacity- the largest population that an environment can support at any given time 2. limiting factor- a factor that limits population growth such as food, water, shelter, space or sunlight Predation-when one organism preys on another organism There are two organisms involved: predator- an animal that hunts other animals prey- an animal that is hunted Symbiosis- a close long term relationship between two different organisms Three types of symbiosis: 1. Mutualism (+/+):both species benefit Ants living in the tropical acacia trees 2. Commensalism (+/0): one species benefits and the other species is unaffected Spanish moss grows on the branches of trees. 3. Parasitism (+/-):one species benefits and the other species is harmed Ticks feed on dogs.