si worksheet 5
advertisement
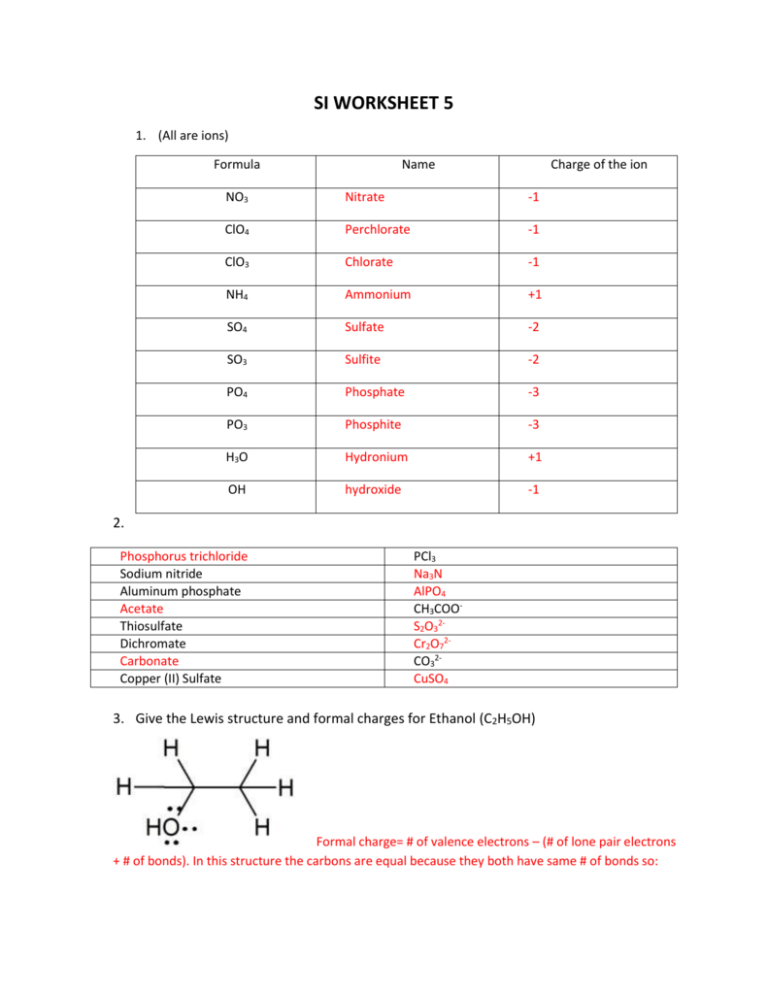
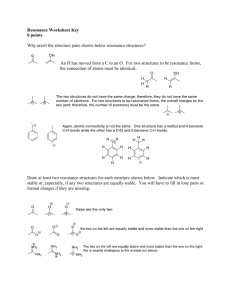
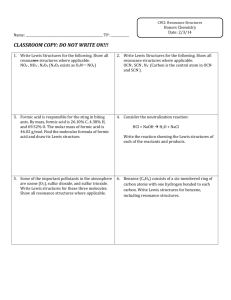
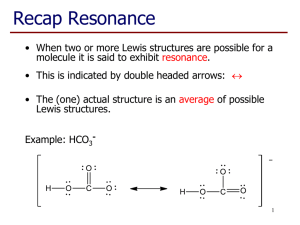
SI WORKSHEET 5 1. (All are ions) Formula Name Charge of the ion NO3 Nitrate -1 ClO4 Perchlorate -1 ClO3 Chlorate -1 NH4 Ammonium +1 SO4 Sulfate -2 SO3 Sulfite -2 PO4 Phosphate -3 PO3 Phosphite -3 H3O Hydronium +1 OH hydroxide -1 2. Phosphorus trichloride Sodium nitride Aluminum phosphate Acetate Thiosulfate Dichromate Carbonate Copper (II) Sulfate PCl3 Na3N AlPO4 CH3COOS2O32Cr2O72CO32CuSO4 3. Give the Lewis structure and formal charges for Ethanol (C2H5OH) Formal charge= # of valence electrons – (# of lone pair electrons + # of bonds). In this structure the carbons are equal because they both have same # of bonds so: Carbon= 4 – (0+4)=0 and oxygen= 6 – (4+2)= 0 so this is a neutral molecule. **Extra lone pair on oxygen does not need to be there 4. Give the Lewis structure, formal charge, and any resonance contributes for sulfate ion. Which resonance contributor(s) are the most prevalent (stable) *The Top row shows the MOST correct way to depict the sulfate ion in a Lewis Structure and its resonance structures. The Bottom row is an acceptable way to draw Sulfate for the purposes of this class and test. Sulfur is in the 3rd row of periodic table and so it can break the octet rule. The top row is most correct because the charges on each atom are minimized. Remember formal charge = val. Electrons – (# of lonepair electrons + #bonds) Top Row: Sulfur: 6 – (0 + 6) = 0 2-Oxygen (with dub. Bond): 6-(4+2)= 0 2- Single bonded oxygen: 6-(6+1)= -1 *2( Bottom figure: Sulfur: 6- (0 + 4) =2 This oxygen isn’t present here 4-single bonded O: 6-(6+1)=-1*4 BOTH SUM TO -2 but the charges are minimized in the top row = more stable 5. Give the Lewis structure, formal charge, and any resonance contributes for phosgene (COCl2). Which resonance contributor(s) is/are the most prevalent (stable) In Good resonance: C: 4 – ( 0+4)= 0; Oxygen: 6 – (4+2)= 0; 2 Cl: 7 – (6+1)=0 In Bad resonance: C: 4- (0+3)= 1; Oxygen: 6 – (6+1) = -1; 2 Cl: 7 – (6+1)=0 6. Draw the Lewis structure and any resonance structures for Thiocyanate ion (SCN-) *The bend in the pictures represents a carbon atom. The middle picture with two double bonds is most stable because the negative charge on the atom resides on the most electronegative atom