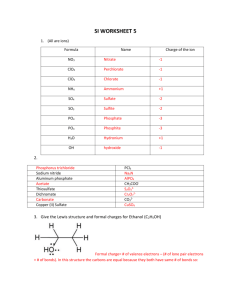
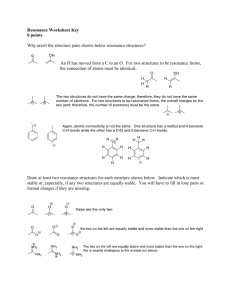
Resonance Structures: Lewis Structures & Valency
advertisement
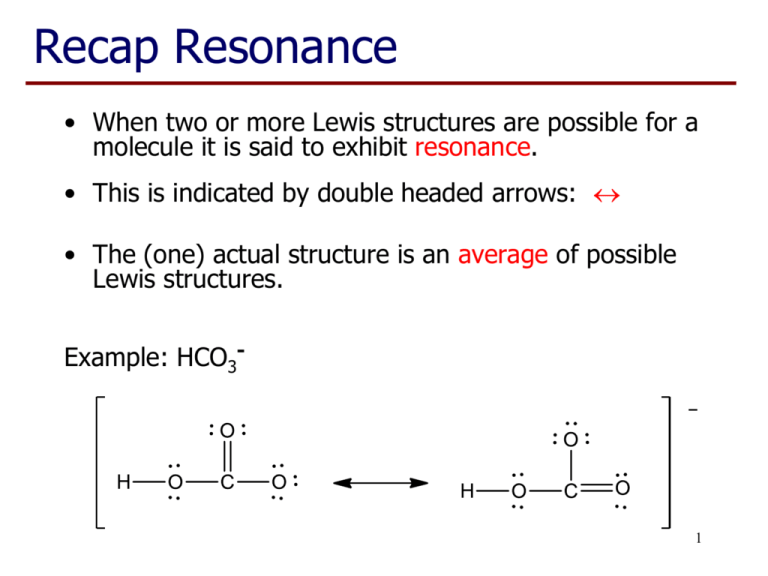
Recap Resonance • When two or more Lewis structures are possible for a molecule it is said to exhibit resonance. • This is indicated by double headed arrows: • The (one) actual structure is an average of possible Lewis structures. Example: HCO3- 1 Recap Lecture 7 • Elements of Period 3 (eg P, S, Cl) have their valence electrons in the third shell • The third shell can hold a maximum of 18 electrons in the s, p & d sub-shells • Consequently we see structures that may have more than 8 electrons associated with these atoms 2 Example: POCl3 Total number of valence electrons: 5 + 6 + (3 x 7) = 32 Oxygen has a valency of 2 so, when uncharged, forms two bonds. 3 Example: POCl3 • P now has 10 electrons, but this is OK as they are in the third shell (max 18 electrons). • O has the two bonds expected from its valency. • These are resonance structures (only position of the electrons have moved) but not ‘equivalent’. • Right hand structure is a better representation of the 4 real structure. Valency and charge • Valency works well for C, N, O & F in neutral molecules. • For period 3 elements (and below) it is only part of the story, eg S forms compounds with 2, 4 or 6 bonds. • If a charge is present, the atom may have more/less bonds than expected. 5 Predicting the best structure • Draw the Lewis structure, including lone pairs and multiple bonds. • Check for the presence of ‘equivalent’ resonance structures. • Check number of bonds on C, N, O & F as a prompt for ‘non-equivalent’ resonance structures. • Choose best structure and check again for resonance structures. 6 Chlorite ion, ClO2Total number of valence electrons: 7 + (2 x 6) + 1 = 20 Note: 8 electrons on oxygen remains fixed, Cl has 8, 10 or 12 electrons 7 Sulfate ion, SO42Total number of valence electrons: 6 + (4 x 6) + 2 = 32 These are all resonance structure but the last one is ‘best’ so far. 8 SO42-, possible structures: 9 Sulfate ion, SO42There are also other resonance structures related to some of these structures. And the real structure is best represented by an average of these six structures. All S-O bonds are the same length.10 Learning Outcomes: • By the end of this lecture, you should: − be able to construct Lewis structures of molecules and polyatomic ions containing period 3 elements − recognise situations where resonance occurs − identify non-equivalent resonance structures − be able to choose the resonance structure(s) that are likely to most closely represent the real structure − be able to complete the worksheet (if you haven’t already done so…) 11 Questions to complete for next lecture: 1. Draw the Lewis structures of NH2-, NH3 and NH4+ and indicate how the number of bonds relates to the valency of nitrogen. 2. Draw the Lewis structure of PCl3 and PCl5 and indicate the number of electrons associated with the phosphorus atom. 3. Draw the ‘best’ Lewis structure of SO2 and SO3 and give a reason for your choice. 4. Draw the ‘best’ Lewis structure of HPO32- and give a reason for your choice (note H is bonded to the P). 12