212-13Con-Anal
advertisement

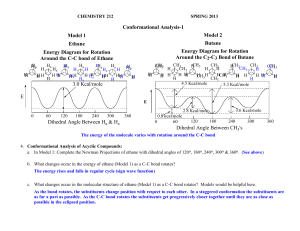
CHEMISTRY 212 SPRING 2013 Conformational Analysis-1 A. References: CGW Ch. 16: pp. 360-366 B. Acyclic Compounds: 1. Conformations: Structures that differ in the positions of atoms due to rotation of -bonds. 2. Method of Representation - Newman Projections: CH3 4 CH Cl 3 Looking down H Cl H the bond from 2 3 H H H C2 <- C3 1CH3 H CH3 R-2-chlorobutane Cl H CH3 The back carbon atom (C2) and its three other bonds CH3 H H The front carbon atom (C3) and its three other bonds 3. Ethane CH3 "Free Rotation" around the C-C bond. \ There is an infinite # of conformations HH H H H Dihedral angle of 60˚ HH H H Dihedral H H angle of 0˚ H Dihedral Angle: Staggered Eclipsed The angle between Easily recognizable the substituents Extreme Conformations on adjacent carbon atoms. CH3 4. Conformational Analysis of Acyclic Compounds: a. In Model 1: Complete the Newman Projections of ethane with dihedral angles of 120o, 180o, 240o, 300o & 360o. (See p. 2) b. What changes occur in the energy of ethane (Model 1) as a C-C bond rotates? c. What changes occur in the molecular structure of ethane (Model 1) as a C-C bond rotates? Models would be helpful here. d. Suggest an explanation for the change in energy as bonds rotate. Conformational Analysis-1 Hxa H Model 1 Model 2 Ethane Energy Diagram for Rotation Around the C-C bond of Ethane Butane Energy Diagram for Rotation Around the C2-C3 Bond of Butane H HH HH 2 Ha H Hx H HH Ha H H HxH H Ha Hx H H HHx HHa Hx HH CH33 CH Ha H H Hxa HHH H H H H H HH CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 HCH3 CH3 H H H HH H H H H H H H H 3H CH H CH3 4.5 Kcal/mole 5.3 Kcal/mole 3.0 Kcal/mole E E 3.6 Kcal/mole 2.8 Kcal/mole 0 60 120 180 240 300 Dihedral Angle Between Ha & Hx 360 0 0.8 kcal/mole 60 120 180 240 300 Dihedral Angle Between CH3's e. In Model 2: Complete the 3 additional Newman Projections of butane with dihedral angles of 240o, 300o & 360o. f. How does the Energy Diagram of Butane (Model 2) compare with that of Ethane (Model 1)? g. Suggest an explanation for the differences between the rotation diagrams for ethane and butane and provide your warrant. 360 3 Conformational Analysis-1 Reflector’s Report Discussion: Identify the most important concepts you learned from this activity: What questions remain? Strategy Analyst’s Report Discussion: How did the use of Newman Projections with ethane and butane help you group formulate a hypothesis on interactions between electron clouds on groups that are not attached to each other in a molecule. How did this activity affect your understanding of how “free” rotation is around -bonds? Out of Class Applications: A. Read: CGW Ch. 16: pp. 360-366 B. Application Questions: 1. Draw a potential energy diagram like those on p. 2 of this activity for rotation around the C2-C3 bond of 2,3-dimethylbutane. Estimate the relative heights of the energy barriers from those in Models 1 & 2. 2. How does your diagram for 2,3-dimethylbutane compare with the diagram for butane (Model 2, p. 2 of this activity)?