nutrition/effects of nutrient deficiencies and their relationships to body structures
advertisement

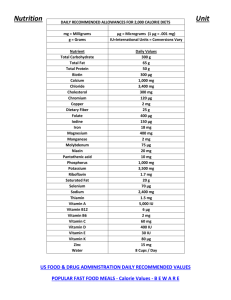
السالم عليكم ورحمة هللا وبركاته Objectives To know basic concepts of Nutrition. To understand that diet has an impact on health. To understand the concept of malnutrition, i.e. under nutrition and over nutrition. To know a variety of dietary related diseases and their associated risk factors, e.g. coronary heart disease, obesity, osteoporosis, iron deficiency and anaemia. INTRODUCTION Nutrients are the constituents of food necessary to sustain normal functions of the body. Macronutrients: -proteins -fats -carbohydrates Micronutrients: -vitamins -minerals 5 Carbohydrates Simple Complex Fiber Protein (Animals and plants) Lipids/Fats Saturated Fat Essential fatty acids: linoleic & linolenic acids Unsaturated Fat Vitamins Minerals/Elements ROLE OF DIFFERENT FOODS Adults should consume 45 to 65% of their total calories from carbohydrates 20 to 35% calories from fats 10 to 35 % calories from proteins. Carbohydrates provide energy and fiber Fats provide energy and essential fatty acids Proteins provide essential amino acids for protein synthesis. ROLE OF DIFFERENT FOODS Vitamins are organic compounds that cannot be synthesized by humans and, therefore must be supplied by the diet. Vitamins have specific biological functions and deficiency of vitamins causes diseases. Minerals are needed for the normal growth and maintenance of the body. MACROMINERALS – minerals that are needed in amounts greater than 100 mg/day by the human body. MICROMINERALS OR TRACE ELEMENTS – minerals that are needed in amounts less than 100 mg/day by the human body. Macrominerals 1.Calcium[Ca] 2.Phosphorous[P] 3.Sodium[Na] 4.Potassium[K] 5.Chloride[Cl] 6.Magnesium[Mg] Microminerals or Trace elements: 1.Iron[Fe] 2.Iodine[I] 3.Copper[Cu] 4.Manganese[Mn] 5.Zinc[Zn] 6.Cobalt[Co] 7.Molybdenum[M] 8.Selenium[Se] 9.Fluoride[F] 10.Chromium[Cr] 11.Silicon[Si]. 13 13 ENERGY REQUIREMENT IN HUMANS Sedentary adults (less activity) require 30 kcal/kg/day. Moderately active adults require 35 kcal/kg/day Very active adults require 40 kcal/kg/day HOW ENERGY IS USED IN THE BODY? The energy is used in the body for three energy requiring processes that occur in the body 1. resting metabolic rate. 2. thermic effect of food (formerly termed specific dynamic action). 3. physical activity. . DISEASES DUE TO NUTRITIONAL FACTORS Over nutrition • Obesity is caused by consuming too many calories compared to the amount of exercise the body is performing, causing a distorted energy balance. It can lead to diseases such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. KWASHIORKOR Kwashiorkor: lack of protein in diet, leading to failure of neural development. “the sickness the older child gets when the next baby is born” Characterized by bloated belly Marasmus Marasmus: progressive emaciation due to lack of protein & calories preventing growth. Cause of 49% of the 10.4 million deaths occurring in children younger than 5 years in developing countries. Noma, Cancrum oris • Cause: under/malnutrition • Problem: secondary infection; mucous membranes become inflamed and develop ulcers, often in the mouth Anemia Cause: iron deficiency, decrease in the number of RBCs Problem: fatigue, irritability, shortness of breath, constant headache Beriberi Cause: lack of vitamin B1 (thiamine) Problem: heart and nervous system damage, muscle wasting, brain damage Goiter Causes: lack of iodine Problem: deafness, fatigue, weight gain, enlarged thyroid Pellagra Cause: lack of niacin Problem: dermatitis, weakness, intestinal distress, neurologic manifestations, organ failure Osteoporosis Cause: lack of calcium and/or (prevents absorption of calcium) vitamin D Problem: weak bones, fractures, decrease bone density Rickets Cause: lack of vitamin D Problem: softening and weakening of bones from release of calcium from bones Scurvy Cause: lack of vitamin C Problem: irritability, swelling and hemorrhage especially over long bones, death from hemorrhage and cardiac failure Xerophthalmia Cause: vitamin A deficiency Problem: blindness Zinc deficiency Cause: diet deficient in zinc Problem: poor wound healing, bone deformities, dwarfism, hyperpigmentation, fetal abnormalities, immune system failure