Plant Structure Review Worksheet
advertisement

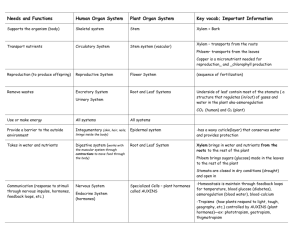
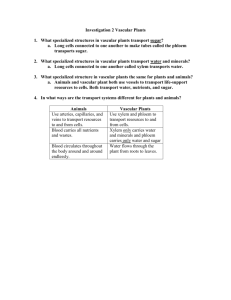
Plant Structure Review Names:___________________ Working with your partner, complete the worksheet. Look up answers you do not know. a. anther _____ 1. a waxy or fatty and watertight layer that covers a plant’s epidermal cells b. antheridium _____ 2. a structure in seedless plants that produces eggs c. archegonium _____ 3. a structure in seedless plants that produces sperm d. cotyledon _____ 4. a horizontal underground stem e. cuticle _____ 5. contains a male gametophyte of a seed plant f. ovule _____ 6. the part of the sporophyte in which the female gametophyte develops g. pistil _____ 7. the transfer of pollen grains from the male to the female reproductive structure h. pollen grain _____ 8. Leaf-like structure that is part of a plant embryo i. pollination _____ 9. a flower structure that consists of a threadlike filament topped with an anther j. rhizome _____ 10. a pollen-producing sac k. stamen _____ 11. the female reproductive structure of a flower _____ 1. blade a. causes a plant’s stems and roots to thicken _____ 2. germination b. permits plants to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide _____ 3. guard cell c. one of a pair of specialized cells that open and close the stomata _____ 4. heartwood d. the broad, flat portion of a typical leaf _____ 5. meristem e. occurs at the tips of stems and roots _____ 6. mesophyll f. the non-conducting older wood in a tree trunk _____ 7. petiole g. ground tissue found in the center of a dicot stem _____ 8. phloem h. a strand that contains both xylem and phloem tissue _____ 9. pith i. the beginning of plant growth from a seed or spore _____ 10. primary growth j. the part of a tree trunk that is active in transporting water and nutrients _____ 11. sapwood k. tissue made of hard-walled cells that transport water and mineral _____ 12. secondary growth nutrients _____ 13. stoma l. ground tissue found in the center of a leaf _____ 14. vascular bundle m. the stalk that attaches a leaf to a plant’s stem _____ 15. xylem n. an area of undifferentiated plant cells that are capable of dividing o. tissue made of soft-walled cells that transport organic nutrients Complete each statement by writing the correct term in the space provided. 16. A type of tissue called ______________________ tissue forms the protective outer layer of a plant. 17. A type of tissue called ______________________ tissue makes up much of the inside of the non-woody parts of a plant. 18. A type of tissue called ______________________ tissue functions in the transport of materials and the support of a plant. Classifying Biologists have classified nonvascular plants, seedless vascular plants, and seed plants based on structural features and patterns of reproduction, many of which are listed below. In columns 1–4, place a check mark in the boxes for the features and patterns found in each type of plant. 1. e 2. c 3. b 4. j 5. h 6. f7. i8. d9. k10. a11. g 1. d 2. i 3. c 4. f 5. n 6. l 7. m 8. o 9. g 10. e 11. j 12. a 13. b 14. h 15. k 16. dermal 17. ground 18. vascular