Why are plants important?
advertisement

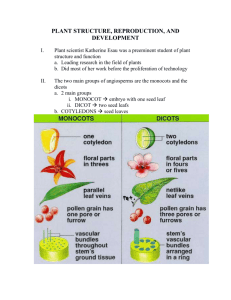
Plant Science All Life Depends on Plants Why are plants important? • Plants Clean the air – by taking in carbon dioxide and producing oxygen. • Make surroundings more attractive • Food • Medicine • Clothing • Housing How does it all relate? Plant Classification 1. BINOMIAL NOMENCLATUREThis is what scientist use to name and group plants. 2. How do we group them together? - grouping plants according to their similarities A. Physical B. Life Cycle 3. The groups are (from largest to smallest) - Kingdom - Phylum - Class - Order - Family - Genus - Species Plant Life Cycles • Life Cycle – The length of time it takes a plant to complete life from germination to death - Measured in growing seasons - Refers to the period of temperatures are favorable for plant growth Life Cycle of Plants 1. Completes its entire life cycle in a single growing season is called ____________ Annuals Usually planted in March – June Dies before the first fall frost 2. Biennial – Completes its life cycle two growing seasons. – Grow during first season reproduce 2nd season How can they do this? store food in their roots Life Cycle of Plants 3. Perennial - Requires 3 or more growing seasons to complete the life cycle. They often reproduce often during their life span. Examples: Apple trees and pines, roses, shrubs. Plant Life Cycle • Summer Annuals – Planted in spring, harvested in fall • Winter Annuals – Planted in fall, harvested in following summer Seed Germination & Seed Growth A. 3 Stages of Growth & development 1. Seed germination & seed growth 2. Vegetative growth 3. Reproduction Seed Germination & Seed Growth B. What factors do we need to consider before planting our crops? 1. Soil Temperature 2. Soil Moisture 3. Seed quality (germination %) 4. Date of Planting 5. Type of soil If we ignore these factors how does it affect our crop? The Leaf Purpose – They are the “factories of the plant”. 2 major parts The Blade & Petiole, Blade- is the flatten part expanded part of a leaf Petiole – is the cylindrical part that attaches to the stem The Leaf Center of the leaf has many cells called chloroplast. They are responsible for photosynthesis Photosynthesis – Chemical process that converts water and co2 to glucose sugar & O2 It is the most important process in the world 2 subclasses for seeds 1. Monocot – has only one seed leaf when it emerges from the soil. • Stored food in endosperm • Veins are parallel. • Ex: corn, wheat, oats, rye, barley (grass plants) Seed Leaves 2. Dicots Plant that has 2 seed leaves when it emerges from the soil. Leaves with network of veins • Vascular bundles form ring outside of stem • Examples: alfalfa, soybeans What is the Purpose of a Stem on a Plant? Vegetative part of the plant that supports leaves, buds, & other organs. Used to help transport food, water & nutrients in a plant Inside the stem contains: Xylem, Phloem, Pith, Epidermis, cortex, & sometimes the cambium Vascular Systems Xylem & Phloem Xylem – Tissues that carries water & minerals from the root hairs throughout the plant. Most fluid movement is upward. Vascular Systems Phloem – Tissue that carries plant products such as glucose from production sites to othe parts of the plant. Fluids are usually moving from leaves to the roots Vascular Systems Cambium – The site of all new cell production in the stem. Creates both Xylem & Phloem If a plant has no cambium – the plant makes all the cells it will ever have during its intial growth. As the plant grows further, these cells just enlarge.