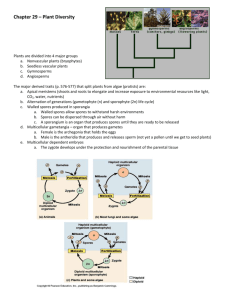
General Plant and Plant cell characteristics: Eukaryotic – contains
advertisement

General Plant and Plant cell characteristics: I. II. III. Eukaryotic – contains usual membrane bound organelles a. Additional structures: i. Chloroplasts – contain chlorophyll; site of photosynthesis ii. Cell wall – made of cellulose and lignin; provides rigidity and protection; slows water loss iii. Central vacuole – stores water for photosynthesis; provides turgor pressure to help with plant’s rigidity Multicellular Autotrophic Plant classifications/divisions: ancient ancestor of plants is green algae (Protist) I. II. Nonvascular or Bryophytes a. Do not contain vascular tissue b. Do not have stems, leaves, or roots i. Contain rhizoids – root-like structures, usually one cell thick to anchor plant c. Rely on osmosis and diffusion to transport water and nutrients in and out of their cells d. Therefore usually very small e. Reproduce through the use of spores (therefore seedless) f. Three subdivisions: i. Mosses ii. Liverworts iii. Hornworts Vascular a. Contain vascular tissue i. Xylem – carries water from roots up to stems/leaves ii. Phloem – carries nutrients up or down to wherever the plant needs iii. Cambium – produces new xylem or phloem as the plant grows b. Contain stems, roots, and leaves c. Reproduction method separates this group further i. Seedless Vascular Plants 1. Reproduce using spores 2. Three subdivisions: a. Ferns i. Leaves = fronds ii. Sori are spore cases on underside of fronds iii. Grow in a variety of habitats iv. Young fronds = fiddleheads are gourmet treat b. Club mosses i. Stems grow along ground ii. Leaves are scale-like iii. Produces powder that can be used in fireworks c. Horsetails i. Small leaves in circular pattern around hollow stem ii. Contain silica – abrasive; used as pioneer’s scrub brush for pots ii. Seed Vascular Plants (see separate notes pdf file)