EOC Review Guide Answers 1
advertisement

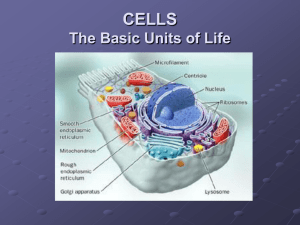
EOC Review Guide Answers 1. Fill in the table below: Macromolecule Protein Carbohydrate What it’s made of Amino acids Sugars, or any combination of carbon, hydrogen & oxygen 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids Lipids Nucleic acids Nucleotides (sugar, phosphate & nitrogen base) Description/test/use Proteins are used for structure and as enzymes Starches, sugars, cellulose makes cell walls, as a fuel for energy Are in fats, oils, & waxes Used to make DNA, RNA, & ATP 2. What are the characteristics of enzymes? What are enzymes used for? Made of __proteins_____. Specific- Enzymes will only work on one specific substrate (the thing the enzyme acts on) Active site- the an area that interacts with the substrate Reusable- enzymes don’t get used up in a reaction, they don’t change at all Reduce the _____activation _ _energy_ of a reaction 3. Comparing cells Prokaryote Nucleoid – the chromosome of the bacterium Chromosome is circular Reproduces by asexually by binary fission or sexually by conjugation Cell walls made of peptidoglycan Eukaryote Cytoplasm Has membrane wrapped organelles like a mitochondria & chloroplast Cell membrane Nucleus ribosomes Usually diploid Cell wall of cellulose or chitin Reproduces asexually by mitosis or sexually by meiosis 1 Plants ___ Animals Centrioles Cell wall Chloroplast Large central vacuole Lysosomes Ribosomes Golgi Apparatus ER Nucleus Mitochondria Cytoskeleton 4. Name that cell part! Organelle What it does Nucleus Cell membrane Contains the chromosomes & runs the cell; the” brains” Carries out cellular respiration to make ATP; “powerhouse” of the cell Carries out photosynthesis, converting radiant energy to chemical energy Made of two protein subunits, helps read mRNA to make a protein Controls what enters and leaves the cell Cell wall Cytoplasm Mitochondria Chloroplast Ribosome lysosome Vacuole Golgi Apparatus Found in a: Prokaryote No Eukaryote Yes Plant Yes Animal Yes No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Yes No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Provides protection & structure to the cell Yes Yes Yes No Liquid part of the cell; lies outside the nucleus Digests invading virus, old cell parts, “recycler” Large, central, water filled structure; holds wastes & nutrients Yes Yes Yes Yes No Yes No Yes No Yes Yes No Packaging center for proteins No Yes Yes Yes 2 5. Virus vs. Bacteria Use the T-chart below to compare virus & bacteria Virus Bacteria 1.) How does it reproduce? Only inside of a host cell Independently by binary fission 2.) What is it made of? Nucleic acid in a protein coat These are cells 3.) Is it free living or parasitic? Must be parasitic Most are independent; some are parasitic 4.) Is it an autotroph or a heterotroph? Neither, it is not alive most are heterotrophs, a few are autotrophs 6. Cell Cycle: Describe what happens in each step of the cell cycle (Interphase through cytokinesis) & make a quick sketch of each. Interphase- cell goes about its daily business, manufactures more proteins & organelles. If it’s going to divide, the chromosomes are copied Prophase- nuclear membrane dissolves, chromosomes coil up and become visible; centrioles, if present, divide and move to poles of cells, spindle fibers begin forming Metaphase- spindle fibers attach to chromosomes; coiled chromosomes are pulled into line across center of cell; centromere divides to end this phase and start the next Anaphase- Centromere divides and sister chromatids are now chromosomes; they move to ppposite poles of the cell Telophase- Chromosomes have arrived at poles of cell & begin to unwind; nuclear membrane begins to reform Cytokinesis- division of the cytoplasm, after the nucleus has divided. In plants it begins with a division plate across the middle of the cell. In animals, it begins with the formation of the cleavage furrow that pinches the cell in two in the middle. 3 7. Diffusion: What is the difference between solutions that are hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic? The difference is in the amount of solute dissolved in the solution that surrounds the cell. What is happening to the cells in the picture below and why? Hypotonic- water moves into cell because the salt concentration in the cell is greater than the salt concentration outside the cell; the cell swells & may burst Isotonic- salt concentration is the same inside & outside the cell; no net movement Hypertonic- more salt in the solution outside the cell; water moves out of the cell ; the cell shrivels 8. Disease: Name 3 ways diseases are spread. a. airborne- spread by droplets released b. person to person- by hand, kissing c. food borne- spread by contaminated food 9. Disease: What is a pathogen? Disease causing organism What kinds of things can be pathogens? Virus, bacteria, parasite What body system protects us against them? Immune system 10. Cellular Energetics. Use the manipulative at station 1 to help you answer these questions: a. Photosynthesis occurs in __plants___ in the organelle called the _____chloroplasts______. b. In photosynthesis, _CO2__+ __H2O__ and the energy of ___Sunlight_ make _C6H12O6_ + _O2___. c. Respiration occurs in all _Cells___ in the organelle called the ___Chloroplast_____. d. In respiration, __C6H12O6__ + ___O2__ make _CO2_ + __H2O_ and make _ATP__ for the cell to use. 11. Levels of Organization: Arrange the following terms in order from lowest level of organization to highest in the space beside them. Atom Tissue Atom.> molecule>organelle>cell>tissue>organ>organ system>Organism> Cell Organ >Species Organelle Organ System Molecule Organism Species Organ system 4 12. Evolution & Diversity: Define the following terms, & tell how each can be used to understand how organisms developed. Analogous structure- Structures that organisms have and that very similar, but only because the organisms have evolved in similar niches Homologous structure- Structures that organisms have that are similar because they have evolved from a common ancestor Vestigial structure- Structures that are reduced in size & function because they are much less used now than they were, so they don’t need to be as large 13. Make a Cladogram using the species cards. Sketch it below. What do we use cladograms to show? Monkey Humans Turtle Kangaroo Fish Frog Amphioxous 14. Diversity/ Taxonomy (or “How do you know it is what it is?”) Think fast game: Play against the other pair at your table. Try to describe the organisms as you pick up the card. Your partner must guess the organism. You may not tell them what it is! After the game, do the following: For each of the organisms listed below, give at least three things that help you to tell it apart from all other types of organisms. Bacteria- prokaryote, heterotroph or autotroph, no organelles or nucleus Protista- Eukaryotic, may have cell walls (algae), may be heterotroph or autotroph, may be unicellular or multicellular Fungi- Eukaryotic, heterotroph, lives on dead materials (or on live organisms if it is parasitic), cell walls made of chitin Fish- Eukaryotic, heterotroph, no cell walls, has a backbone, body covered with moist scales, 2-chambered heart, cold blooded Plant- Eukaryotic, autotroph, multicellular, cell walls are made of cellulose, photosynthetic Reptile- Eukaryotic, heterotroph, no cell walls, has a backbone, body covered with hard, dry scales, 3-chambered heart, cold blooded, lays a leathery shelled egg Mammal- Eukaryotic, heterotroph, no cell walls, has a backbone, body covered with fur or hair, 4 chambered heart, warm blooded Bird- Eukaryotic, heterotroph, no cell walls, has a backbone, body covered with feathers, 4 chambered heart, warm blooded, lays a hard shelled egg Invertebrate- Eukaryotic, heterotroph, no cell walls, has no backbone, body may be covered with an exoskeleton, a shell, or some other body covering, circulatory system may be open or closed 14. What are the levels of classification, in order? Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, species The scientific name consists of the genus and species name, underlined. Organisms that have the same genus name are very closely related. Each level is made of several groups from the level that comes after it. (For example, a kingdom is made of several Phylums, a Phylum is made of several Classes, etc.) 5 15. Cell theory: What does the cell theory say? (Hint: there are three parts to it.) All living things are made of cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure & function in a living cell. Cells come only from pre-existing cells. 16. At the 4th station, Use the DNA cards to make a complementary strand of DNA. molecule sequence. What is this process called? DNA TAC Write down both sides of your DNA GGC AAA T T T CCC ATC DNA ATG CCG T T T AAA GGC TAG Now use the RNA cards to make a messenger RNA from the original DNA strand. Write down the DNA sequence and the RNA sequence. What is this process called? DNA TAC GGC AAA T T T CCC ATC RNA AUG CCG UUU AAA GGG UAG Now, use the decoder sheet to choose and line up the Amino acid sequence in the correct order. Write down the amino acids. What is this process called? Met-Pro-Phe-Lys- Gly-Stop 17. Which two of the above named processes is used to make a protein? Transcription and then Translation Which process will a cell use to pass on genetic information just before it divides? Replication 18. Genetics: Define the following: (Note: Remember that alleles are different versions of the same gene, and that most organisms are diploid, so there are two genes (alleles) in the genotype, like AA or Aa or aa.) Homozygous- two alleles are alike Heterozygous- two alleles different (one dominant and one recessive) Dominant- the trait that is seen even if only one of the alleles is dominant Recessive- for the trait to be seen, it must be homozygous Incomplete dominance- the offspring look like a blend of the parental traits, there is no clear dominant or recessive trait Phenotype- the physical appearance of an individual Genotype- the genes the individual has 6 19. Work the following cross: A heterozygous dominant purple pea plant is crossed with a homozygous recessive white pea plant. What percent of their offspring will be white? P P 0% white 100% purple PP x pp p p Pp Pp Pp Pp Cross two of their offspring. What percent of the F2 generation will be purple? P p Pp xPp 75% Purple P Pp Pp 25% White p Pp Pp 20. Using the materials at the table, take the organisms shown and build 1) two food chains, 2) a food web and 3) an energy pyramid. 1) Grass > cricket > frog > fox 2) Eagle Frog Snail Fox Raccoon Cricket Grass Rabbit Tree 3) On your pyramid, label the trophic levels and tell what percent of the energy at each level will transfer to the next level 10% of the energy only is transferred to the next trophic level. Eagle Frog Snail Grass Fox Tertiary consumers Raccoon Cricket Rabbit Tree Secondary consumers Primary consumers Producers 7