2.2 Molecules and Compounds notes
advertisement

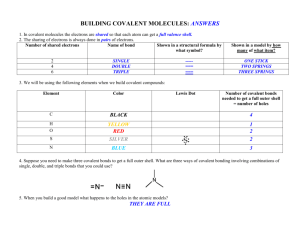
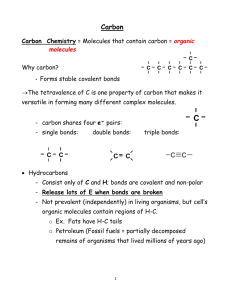
2.2 Molecules and Compounds 1. Ionic Bonding a. Non-metal and metal b. Electrons are transferred from one atom to another (high ΔEN) c. Metal (less e- in valence shell ) donate, non-metal (more e- in valence shell) d. Goal is to have a complete octet in valence shell e. Ions are held together by an ionic bond where positive and negative ions attract f. Draw diagram 2. Covalent Bonding a. Two non-metals b. Electrons are shared between two atoms c. Single, double, and even triple bonds are possible between two atoms. E.g. H2O,CO2, N2 d. We call the substance formed though covalent bonding a molecule e. Shape of molecules i. Molecules have 3-D shape ii. Shapes are necessary to structural and functional roles that molecules play in living things. E.g. hormones need to be a specific shape to be recognized by cells in the body iii. Shape is predicted using VSEPR theory that states that valence shell electron pairs want to get as far away from each other as possible f. Polar vs. Nonpolar Covalent Bonds i. Electrons are shared, but they may not be shared equally ii. Polar molecules (or sections of large molecules) are hydrophilic and nonpolar are hydrophobic, therefore they do not mix iii. Nonpolar bonds = equal sharing 1. Diagram iv. Polar bonds = unequal sharing 1. Dipoles exist (slight negative and positive ends) 2. Allows for weak bonds between molecules 3. diagram v. Due to ΔEN of the two atoms involved in bonding 1. EN is the ability of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons 2. F is the most electronegative 3. EN increases across a row (left to right) and up a column (bottom to top) in Periodic Table 4. diagram g. Hydrogen Bonding i. Polarity in water allows for weak bonds to form between molecules called hydrogen bonds ii. Can also occur wherever a O-H or N-H bond occurs iii. Usually represented by a dotted line to indicate weak nature iv. Though it’s weak, this bond is extremely important in biology, for example, it holds the two strands of the double helix of DNA together and also determines the secondary structure of a protein (more on this later in the unit) v. Diagram