Biology I Notes
advertisement
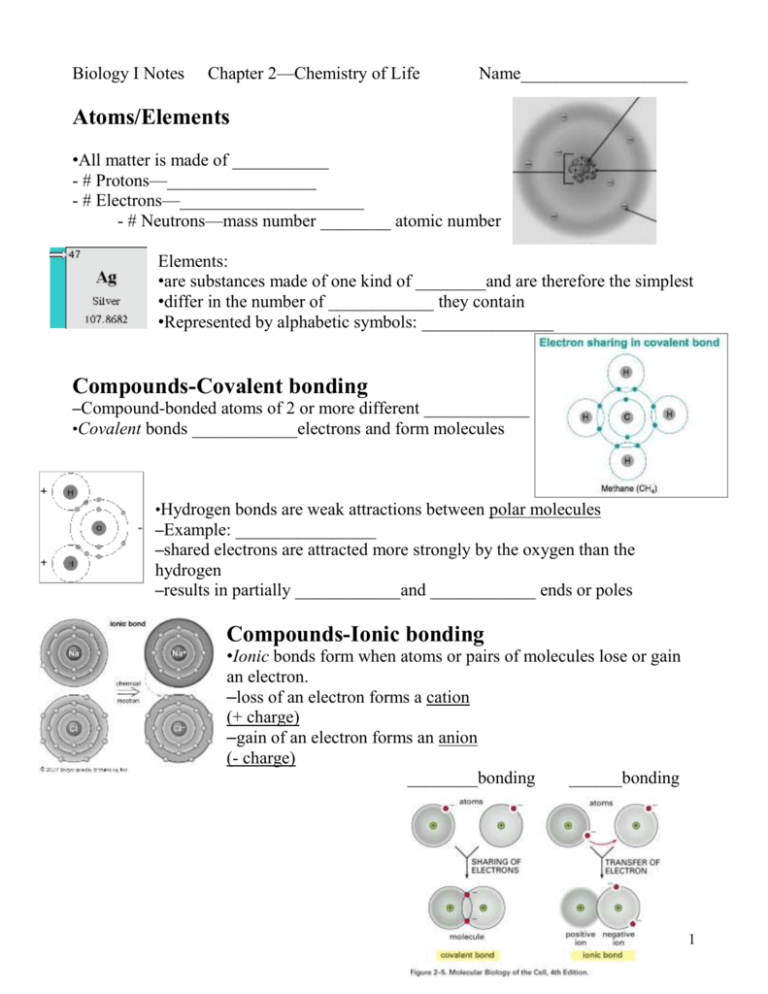
Biology I Notes Chapter 2—Chemistry of Life Name___________________ Atoms/Elements •All matter is made of ___________ - # Protons—_________________ - # Electrons—_____________________ - # Neutrons—mass number ________ atomic number Elements: •are substances made of one kind of ________and are therefore the simplest •differ in the number of ____________ they contain •Represented by alphabetic symbols: _______________ Compounds-Covalent bonding –Compound-bonded atoms of 2 or more different ____________ •Covalent bonds ____________electrons and form molecules •Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions between polar molecules –Example: ________________ –shared electrons are attracted more strongly by the oxygen than the hydrogen –results in partially ____________and ____________ ends or poles Compounds-Ionic bonding •Ionic bonds form when atoms or pairs of molecules lose or gain an electron. –loss of an electron forms a cation (+ charge) –gain of an electron forms an anion (- charge) ________bonding ______bonding 1 The number of times an atom can bond to another atom is determined by the number of ________________ in the __________________________. •The first shell can hold _________ •The second shell can hold __________ •The third shell can hold _________ Water and Solutions Properties of Water •______ of the body is water •______of the molecules in the body are water molecules •assists in temperature regulation—maintaining _______________ –Cohesion is an attraction between substances of the ___________________ •the _________bonds between water molecules cause the cohesion of liquid water •Molecules at the surface of water link together to create __________________ •Ex: water molecules to ________________________ –Adhesion is an attraction between ______________ substances •Seen in plants as capillary action as water is attracted to the _________________ more strongly than __________ pulls it down, allowing stems and leaves to acquire the water they need. •Ex: water molecule to glass surface on side of ____________________ The Universal Solvent-_______________ •Water’s ___________ permits it to dissolve many substances •__________-polar substances like ______ do NOT dissolve well in water pH •indicates the number of charged_____________ atoms in a solution •acids have a pH ___________ 7 and form ________________when dissolved in water •bases have a pH ___________ 7 and form ________________when dissolved in water •water is considered _________________ •pH scale (p.33) 2 Organic CompoundsCARBOHYDRATES -Made of ___________ in a ratio of ____________ -____________, galactose, fructose -Common processes involving organic compounds _________________________—combines 2 sugar molecules (monosaccharide) to form a disaccharide or a polysaccharide made of many _________________________ – ____________________—occurs when carbohydrates consumed as food are broken apart to form simple sugars » requires one _______________________________ » opposite of __________________________ LIPIDS Made of ____________but in a much greater ratio than carbohydrates Store more energy than _________________________ Contained in _________________ cell membranes Saturated vs. Unsaturated o saturated fats are solid at ____________________________ o unsaturated fats are generally ___________at room temperature 3 PROTEINS • • • • A chain of molecules called _________________ ___________ different amino acids builds muscle, skin, ligaments, bones, hair, etc. Made of _______________________ NUCLEIC ACIDS • Made of C, H, O, N, ________ • __________ • __________ CHEMICAL REACTIONS – Absorb or release energy when • Chemical bonds are _____________ • Chemical bonds are _____________ – Need energy to begin—called _________________________ ENZYMES – Most are _________________ – Increase the speed of chemical reactions in __________________ – Very specific • Act on substances called ______________________ • The active site of the enzyme determines which substrate it can act on • Fig. 2-15 (p 41) – Affected by • _______________ • __________ 4