(Start) Carbon Chemistry
advertisement
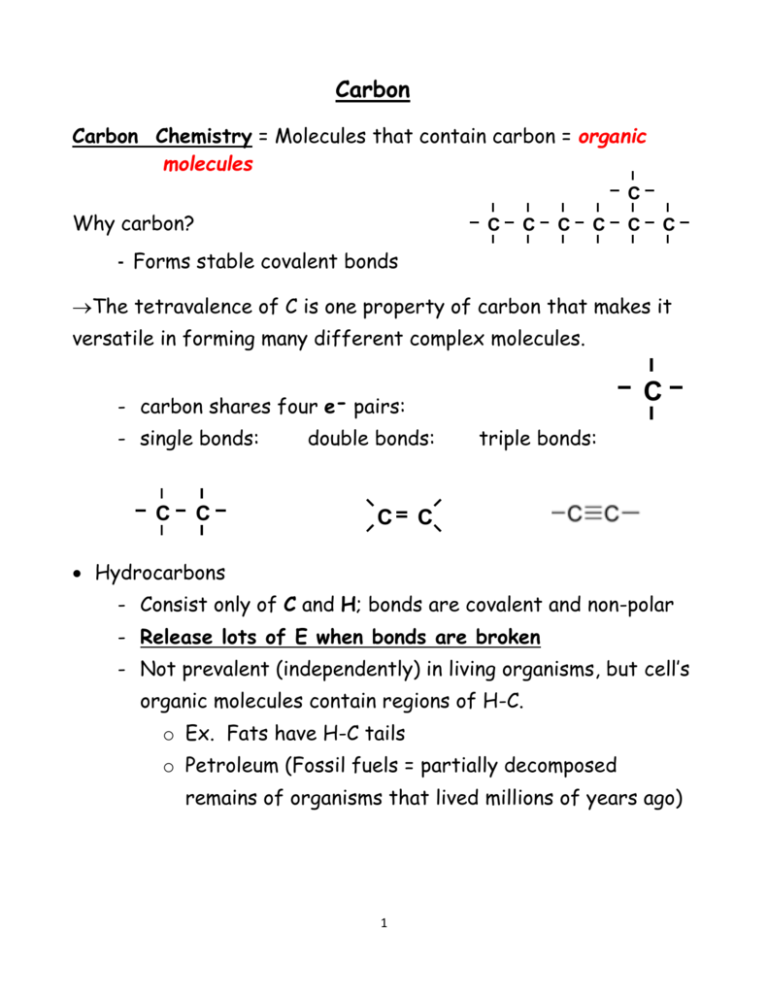
Carbon Carbon Chemistry = Molecules that contain carbon = organic molecules C Why carbon? C C C C C C - Forms stable covalent bonds The tetravalence of C is one property of carbon that makes it versatile in forming many different complex molecules. C - carbon shares four e- pairs: - single bonds: C C double bonds: C triple bonds: C Hydrocarbons - Consist only of C and H; bonds are covalent and non-polar - Release lots of E when bonds are broken - Not prevalent (independently) in living organisms, but cell’s organic molecules contain regions of H-C. o Ex. Fats have H-C tails o Petroleum (Fossil fuels = partially decomposed remains of organisms that lived millions of years ago) 1 Functional Groups / Characteristics Organic molecules have different properties as a result of their structures which is dependent on their functional groups. If the functional group is the variable portion of the molecule = R Group Hydroxyl group – attract water, helping to dissolve organic compounds Carboxyl group – form acids (has own source of H+) hydrophilic & polar (due to electronegative O atom) Amino group – form bases (can pick up H+ from solution) Phosphate group – can transfer ‘E’ between organic molecules ester Carbonyl group – characterizes sugars Aldehydes Keytones ether Sulfhydryl group – helps stabilize protein structure - hydrophobic and non-polar 2 Carbon atoms are named for # of C atoms ~ 1st part of name: a. b. c. d. e. 1 = meth2 = eth3 = prop4 = but(“e”)5 = pent- f. g. h. i. j. 6 = hex7 = hept8 = oct9 = non10 = dec ….and # of bonds ~ 2nd part of name a. b. c. Single bond = alkANE Double bond = alkENE Triple bond = alkyne 3 Numbering Carbons in ring form: Start at the right of oxygen in the ring and move your way around. This will be helpful when understanding the structure of DNA! 4