electric cells
advertisement

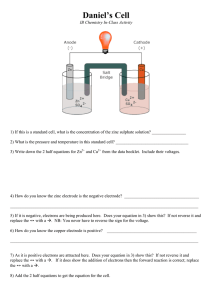
electric cells a simple electric cell a simple electric cell consists of two different metal electrodes placed in an electrolyte metals high up in the reactivity series give up electrons more readily; negative electrode in the cell metals low down in the reactivity series will be the positive electrode in the cell voltage of electric cell depends on the positions of the two metals in the reactivity series; the farther apart they are, the higher the voltage use of electric cell: portable energy such as batteries portable energy: batteries electric cells a simple electric cell consists of pieces of Cu and Zn metals in a solution of NaCl zinc being more reactive than Cu is the negative electrode; Cu metal is the positive electrode zinc metal (negative electrode) voltmeter - + copper metal (positive electrode) NaCl(aq) electric cells a simple electric cell at the Zn electrode, Zn atoms give up electrons to form Zn2+ ions Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e- at the Cu electrode, Cu2+ ions take in electrons to give Cu atoms Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) overall reaction Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s) positive ions are form cations metals or H2 are discharged at are produced at an example is electroplating cathode gives electrons to battery moving ions is negative electrode in decomposes electrolysis takes electrons from anode is reactive metals an example is are discharged at non-metals anions form contains ionic compound (molten/solution) electrolyte is positive electrode in are produced at Cr-plating are negative ions copper aluminium