File
advertisement

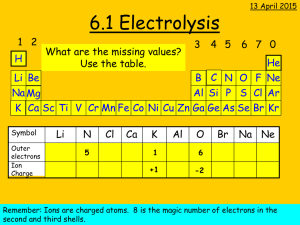
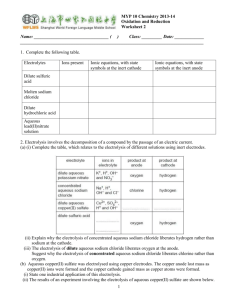
DAILY QUESTIONS • Circle the oxidized element, underline the reduced element. 2Sr +O2 2SrO Fe+2 +O2 FeO • Define what happens to elements that are oxidized and reduced. OBJECTIVES: C5.1 State that electrolysis is the chemical effect of electricity on ionic compounds, causing them to break up into simpler substances, usually elements C5.2 Use the terms electrode, electrolyte, anode and cathode C5.4 Describe the electrode products, using inert electrodes, in the electrolysis of: • molten lead bromide • aqueous copper chloride • dilute sulfuric acid ELECTROLYSIS APPARATUS Electrode - an electrical conductor which carries charge to or from a liquid undergoing electrolysis. Electrode Electrode Electrolyte - a molten or aqueous solution through which an Electrolyte electrical current can flow. ELECTROLYSIS APPARATUS Anode: The positively charged electrode. Attracts negatively charged ions (anions). Anode + - Cathode: The negatively charged electrode. Attracts positively charged ions (cations). Cathode Electrolyte • Electrolysis only happens in: - molten ionic liquids or - aqueous solutions containing ions. • There must be a complete circuit. • A lamp or ammeter can be used to show that electricity is flowing around the circuit. ELECTROLYSIS OF ZINC CHLORIDE In your journal: Describe what is occurring during the electrolysis of zinc chloride. ELECTROLYSIS • Introducing electricity to a mixture can cause a chemical reaction to occur. • However, this requires that the atoms involved become ions • Define ions FORMING IONS Na Cl FORMING IONS Na Cl Na+ Cl- BONDING The outer shell is full, but the ions are not neutral. How can neutrality be achieved? Na+ Cl- IONIC BONDING An ionic bond is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions [Na]+ [Cl]- LET’S TRY A FEW • Lithium & Fluorine • Magnesium & Fluorine CONDUCTIVITY Conductivity is the ability of a substance to conduct electricity. For a substance to conduct electricity, “free” electrons have to be available Free electrons = electrons that are able to move CONDUCTIVITY IN METALS • • • • Electrons move Metals can be in solid or liquid form No chemical change takes place Examples: copper wire; aluminum pan CONDUCTIVITY IN IONIC COMPOUNDS • Ions move • Ionic compounds can be in liquid (molten) form or in aqueous solution • Chemical change takes place • Examples: molten lead bromide, sodium chloride solution, copper(II)sulfate solution AT THE ELECTRODES Cathode (-) (negative electrode) Positive ions go here (cations). As metal ions are positive, they go to the cathode. Ions gain electrons. They are reduced and become neutral atoms. Anode (+) (positive electrode) Negative ions go here (anions). As non-metal ions are negative, they go to the anode. Ions lose electrons. They are oxidised and become neutral atoms (which react together to form molecules). ELECTROLYSIS OF COPPER CHLORIDE In your journal: For the electrolysis of copper chloride: 1. Identify the ions present in the electrolyte. 2. Describe the movement of ions. + Electrolyte: CuCl2 (aq) ELECTROLYSIS OF SOLUTIONS – CATHODE For solutions of highly reactive metals: Hydrogen gas, not the metal, is produced at the cathode. For metals that are more reactive than hydrogen, the metal will stay in the solution and hydrogen gas will be produced. ELECTROLYSIS OF SOLUTION - CATHODE ELECTROLYSIS OF SOLUTIONS-ANODE The product at the anode depends on: The negative anions present in the solution. • • • • Homework: Read the lab report Grade based on the rubric provided Missing CourseworkCome in Thursday Missing homework- fill form then turn in.