Chapter 8 “The Progressive Era” Vocabulary Section 1: The Drive for
advertisement

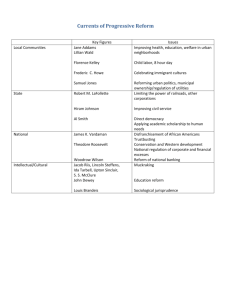
Chapter 8 “The Progressive Era” Vocabulary Section 1: The Drive for Reform 1. Progressivism – movement that responded to the pressures of industrialization and urbanization by promoting reforms. 2. Muckraker – writer who uncovers and exposes misconduct in politics or business. 3. Lincoln Steffens – A muckraker; managing editor at McClure’s, a magazine known for uncovering social problems; published The Shame of the Cities in 1903, a collection of articles on political corruption. 4. Jacob Riis - A muckraker; a photographer for the New York Evening Sun; turned his camera on the crowded, unsafe, rat-infested tenement buildings where the urban poor lived; published several works between 1890 and 1903, including How the Other Half Lives. 5. Social Gospel – reform movement that emerged in the late nineteenth century that sought to improve society by applying Christian principles. 6. Settlement House – Community center organized at the turn of the twentieth century to provide social services to the urban poor. 7. Jane Addams – A leading figure in the settlement house movement; opened Hull House, a settlement house in Chicago, in 1889; inspired other college-educated, middle-class women to become social workers. 8. Direct Primary – Election in which citizens themselves vote to select nominees for upcoming elections. 9. Initiative – Process in which citizens put a proposed new law directly on the ballot. 10. Referendum – Process that allows citizens to approve or reject a law passed by a legislature. 11. Recall – Process by which voters can remove elected officials from office before their terms end. Section 2: Women Make Progress 12. Florence Kelley – Believed that women were hurt by the unfair prices of goods they had to buy to run their homes; helped found the National Consumers League (NCL) in 1899; helped form the Women’s Trade Union League (WTUL) that tried to improve conditions for female factory workers. 13. National Consumers League (NCL) – Group organized in 1899 to investigate the conditions under which goods were made and sold and to promote safe working conditions and a minimum wage. 14. Temperance Movement – Movement aimed at stopping alcohol abuse and the problems created by it. 15. Margaret Sanger – Believed that family life and women’s health would improve if mothers had fewer children. Opened the country’s first birth-control clinic in 1916; founded the American Birth Control League in 1921 to make information available to more women. 16. Ida B. Wells – Former slave, who worked as a school teacher and bought a local newspaper, renamed Free Speech; wrote about the mistreatment of blacks, and helped organize women’s clubs to fight for African American rights. 17. Suffrage – the right to vote. 18. Carrie Chapman Catt – President of the NAWSA in 1900, studied law, and worked as one of the country’s first female school superintendents; best known for her “winning plan” and her “society plan.” 19. National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA ) – Group founded in 1890 that worked on both the state and national levels to earn women the right to vote. 20. Alice Paul – Raised in a Quaker home; helped organize women to recruit other across the nation; formed the National Woman’s Party (NWP), which used public protest marches. 21. 19th Amendment (1920) – Constitutional amendment that gave women the right to vote. Section 3: Struggle against Discrimination 22. Americanization – Belief that assimilating immigrants into American society would make them more loyal citizens. 23. Booker T. Washington – Most famous late 19th century black leader who argued that African Americans needed to accommodate themselves to segregation, instead of trying to overturn the Jim Crow Laws. 24. W.E.B. DuBois – Black leader who criticized Booker T. Washington’s willingness to accommodate southern whites; argued that blacks should demand full and immediate equality and not limit themselves to vocational education. 25. Niagara Movement – Group of African American thinkers founded in 1905 that pushed for immediate racial reforms, particularly in education and voting practices. 26. National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP) – Interracial organization founded in 1909 to abolish segregation and discrimination and to achieve political and civil rights for African Americans. 27. Urban League – Network of churches and clubs that set up employment agencies and relief efforts to help African Americans get settled and find work in the cities. 28. Anti-Defamation League – Organization formed in 1913 to defend Jews against physical and verbal attacks and false statements. 29. Mutualistas – Organized group of Mexican-Americans that make loans and provide legal assistance to other members of their community. Section 4: Roosevelt’s Square Deal 30. Theodore Roosevelt – Became president in 1901; Assistant Secretary of the Navy during McKinley’s Presidency; formed the Rough Riders during the Spanish-American War; became president after McKinley was assassinated; best known for his “Square Deal” program. 31. Square Deal – President Theodore Roosevelt’s program of reforms to keep the wealthy and powerful from taking advantage of small business owners and the poor. 32. Helpburn Act – 1906 law that gave the government authority to set railroad rates and maximum prices for ferries, bridge tolls, and oil pipelines. 33. Meat Inspection Act – 1906 law that allowed the federal government to inspect meat sold across state lines and required federal inspection of meat processing plants. 34. Pure Food and Drug Act – 1906 law that allowed federal inspection of food and medicine and banned the interstate shipment and sale of impure food and the mislabeling of food and drugs. 35. John Muir – California naturalist, whose efforts had led Congress to create Yosemite National Park in 1890; he was interested in preservation. 36. Gifford Pinchot – Led the Division of Forestry in the U.S. Department of Agriculture during Roosevelt’s presidency; recommended that the forests be preserved for public use; he was interested in conservation. 37. National Reclamation Act – 1902 law that gave the government the power to decide where and how water would be distributed through the building and management of dams and irrigation projects. 38. New Nationalism – Former President and Progressive Party candidate Theodore Roosevelt’s plan to restore the government’s trust busting power. 39. Progressive Party – Political party that emerged from the Taft-Roosevelt battle that split the Republican Party in 1912. Section 5: Wilson’s New Freedom 40. Woodrow Wilson –Democratic candidate; helped by William Jennings Bryan to win the Democratic nomination; Doctoral thesis, Congressional Government; known best for his ideas in the program called “New Freedom.” 41. New Freedom – Woodrow Wilson’s program to place government controls on corporations in order to benefit small businesses. 42. Sixteenth Amendment – 1913 constitutional amendment that gave Congress the authority to levy an income tax. 43. Federal Reserve Act – 1913 law that placed national banks under the control of a Federal Reserve Board, which runs regional banks that hold the reserve funds from commercial banks, sets interest rates, and supervises commercial banks. 44. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) – Government agency established in 1914 to identify monopolistic business practices, false advertising, and dishonest labeling. 45. Clayton Antitrust Act – 1914 law that strengthened the Sherman Anti-Trust Act.