Ancient Egyptian Civilization
advertisement

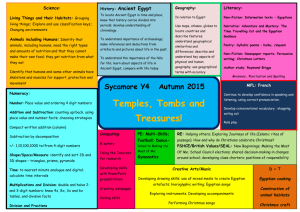
Notes- Ancient Egyptian Civilization Name _______________________________ Period _________ Ancient Egyptian Civilization Chapter 4 Lesson 3 in the World Text The Big Picture Neighboring ____________ were growing while Egyptian _____________was spreading along the Nile. • • • • To the ________, people in Europe were developing the islands and peninsulas across the ___________________________ (2 words). To the _________, Africans were finding ways to survive in the _________desert environment of the Sahara. To the ___________, the kingdoms of Nubia had ________ mines and _________networks that made the kingdom thrive. Asian communities that were large and small on the ________ were ____________today’s countries of Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, and Iraq. The Big Picture…continued ____________and _______________ of people and ideas helped shape development in all of the cultures. Each culture _________________ resources, products, and ideas. New Rulers in Egypt When the Old Kingdom ________________, a new era of Egyptian history began. • Egypt’s __________________________ (2 words) took place about 2100 BC through 1700 BC. When the pharaoh’s armies conquered kingdoms in ________ they made use of gold mines. • The name of this country may come from the Egyptian word for “________,” meaning gold. New Rulers in Egypt…continued During this time, people began moving. • Egyptian traders ___________ their business with cities in western Asia, so people from Asia came to live in Egypt’s _________ region. • By 1650 BC these new settlers, called _____________, challenged the pharaoh. The Greek phrase for Hyksos is “_______________________________.” • This group ruled Lower Egypt for the next _______ years. Notes- Ancient Egyptian Civilization Name _______________________________ Period _________ New Rulers of Egypt…continued The ______________these people use to defeat Egyptian armies in battle: • _____________, chariots, strong bronze weapons, __________, and arrows. Egyptian leaders at ___________continued to control Upper Egypt. In 1550 BC Pharaoh ____________ and the Egyptians regained control of the delta from the Hyksos by using weapons and chariots that they copied from the Hyksos. The _______ Kingdom began when the Hyksos were defeated. • Pharaoh Ahmose and later pharaohs vowed they would become the ______________military power in the world by never letting any outsiders control any part of Egypt. Expansion and Trade During the New Kingdom period, Egypt’s leaders worked hard to win back the __________lost in wars. • • They took control of an area that is now the country of __________, and pushed as far as the ______________ River. ___________: a group of lands and people ruled by one government. Expansion and Trade…continued Country Goods Greece Silver, olive oil. Lebanon Silver, copper, timber, wine. Egypt Grain, bronze goods, papyrus, linen, jewelry. Nubia Gold. Kush Ebony, ivory, animal hides, gold, copper, and precious stones. Punt Gold, perfume, ivory, incense, apes. Expansion and Trade…continued Treasures moved from Kush to Egypt by ___________of men and pack animals. Notes- Ancient Egyptian Civilization Name _______________________________ Period _________ • Soldiers that traveled w/ the trading caravans kept Egypt’s pharaoh’s treasures __________. Large castle-like forts scared away __________along the upper Nile. Products such as ____________ and ___________ were made from raw materials by Egyptian craft workers for Egypt’s pharaoh and wealthy families. Expansion and Trade…continued Egyptian’s traveled from _________ to ________when they used both the Nile River and land travel. Hatshepsut Hatshepsut was the name of one of Egypt’s few _____________ rulers. • Hatshepsut means, “foremost of the noble ladies.” She became _____________ because her husband died and she declared her brother too young to rule on his own. ________________: A group of people who go on a trip for a set reason. Hatshepsut…continued Hatshepsut traded _____________, ____________, and bronze weapons w/ the country of Punt. • Hatshepsut’s ___________, soldiers, artists, and attendants brought back from Punt gold, perfume, ivory, live apes, leopard skins, and rare incense trees. Hatshepsut’s expedition lasted ____years; they traveled by ship and land. Moving Ideas Ideas, trade goods, and skills _________ as Egypt trades with other countries. • Egyptians became _____________________ (2 words) for their understanding of: • Medicine, mathematics, and astronomy. Priests learned their skills in ____________schools. • • The first medical textbooks were written by __________ when writing was invented. The textbooks told doctors how to cure __________, stitch together cuts, and set broken ___________. Moving Ideas…continued Wounds were cured by __________ bread and upset stomachs by _____________. Egyptian priests developed _______________ rules. Notes- Ancient Egyptian Civilization Name _______________________________ Period _________ Moving Ideas…continued The “stars that know no rest” are known to us as the _____________. The “meetings of the Sun and Moon” which created darkness are called ________________. The 2 __________________ we use today that were created by the ancient Egyptians were the: • • 365 day ________________ The ___________ Tutankhamen’s Tomb Located in the ______________________________ • The resting place of _____ New Kingdom pharaohs Tutankhamen ruled Egypt from the time he was 9 until he died at the age of _______. Tutankhamun’s tomb remained _______________ for over __________ years. Tutankhamen’s Tomb…continued The tomb was discovered in ________ by two British archaeologists named Howard ____________ and Lord _______________. The _____________found in his tombs, including the clothes____________ us about how the ancient Egyptians really ______________ like.