Transport of Molecules Notes
advertisement

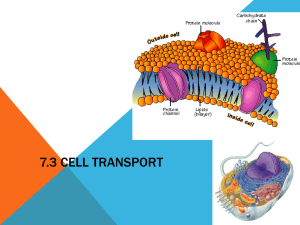
Name:________________________ Period:___________ Notes: TRANSPORT THROUGH CELL MEMBRANES Cells are surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane which allows some materials to enter and exit the cell. Only materials that are dissolved in a solution can be transported across the cell membrane. METHODS OF CELL TRANSPORT __Diffusion/Osmosis___________________________________ __Facilitated diffusion_________________________________ __Active Transport: endocytosis & exocytosis________________ DIFFUSION The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Concentration: The number of molecules of a substance in a given volume. High concentration: More molecules of solute Low concentration: Less Solute: molecules of solute Substance that dissolves in the liquid Solvent: Liquid part in a solution Concentration: amount of a solute in a given solution The molecules have natural random motion , which they use to move from one area to another. Molecules continue to move until they reach equilibrium When the molecules have spread out _evenly__ the solution is said to be in equilibrium. DIFFUSIN ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE The cell membrane is made up of two layers of lipids and proteins. There are openings called __Pores___ in the cell membrane. DIFFUSION CAN OCCUR ONLY IF: The concentration on one side of the cell is _higher____ and the concentration on the other side is _lower_____ Molecules must be __smaller____ than the pores in the cell membrane Diffusion is passive: The cell does not use its own energy to move the molecules. OSMOSIS: The diffusion on ONLY __water___ molecules. Water moves from an area of _high__ concentration to an area of _lower___ concentration. A cell will___burst________ if too much water enters The cell will__shrink_____ if too much water leaves. Dilute solution: very _high___ number of water molecules, low number of solute molecules. Concentrated solution: very low number of ___water molecules._ 1. Passive Transport: No energy required Ex: Diffusion, Osmosis and facilitated diffusion Facilitated diffusion: Movement of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane with a _transport proteins___. Used to move large molecules 2. Active Transport: The movement of substances across a cell membrane using _energy___ Move substances from _Low____ to __hign___ concentration Endocytosis: molecules __enters_________ the cell. Exocytosis: molecules __exit____ the cell.