Transport across Cell Membrane - Mercer Island School District
advertisement

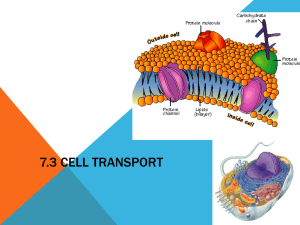
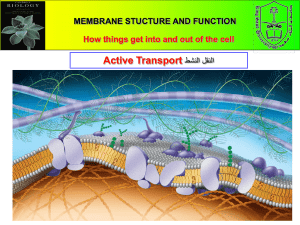
Name: ________________________________________ Period: _______ Online Textbook Virtual Tour: Transport Across the Cell Membrane Directions: Go to http://my.hrw.com and login (student # for both name and password). Choose “Student Premium” options once the e-textbook is open. Select “Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function” at the top of the page and click on “go”. Open the multimedia lab and Virtual investigations and select “Chapter 3: Transport Across Cell Membrane”. Run through all 4 parts and answer the following questions. Part 1: Cell Membranes 1. The cell membrane is composed of _______________________ molecules and _________________________ molecules. 2. Label the phospholipid indicating which regions are polar and non-polar. 3. In water, phospholipids spontaneously form lipid __________________, as the ____________ heads of the molecules are attracted to water while the ______________ tails of the molecules are repelled. 4. The energy needed to move molecules through the membrane depends on the _________ , _____________ , ___________ , and ________________________ of the substances being moved. Part 2: Passive Transport 5. Define Concentration: Concentration gradient: 6. Substances move from an area of ___________________ concentration to an area of ________________ concentration. This movement down the concentration gradient is called _____________________. 7. Passive transport is transport that _____________________ use the cell’s energy. It relies on ____________________ due to a concentration gradient. 8. The diffusion of one substance is generally ________________________ of the diffusion of other substances. 9. Polar molecules and ions are ___________________ by the __________________interior of the phospholipid bilayer, and therefore do not pass through the cell membrane as easily as non-polar molecules. 10. Specific channel ______________ and carrier ____________ that are embedded in the membrane “ _____________” the diffusion of polar molecules and ions. 11. Water molecules are _________________, so the diffusion of water through the membrane is facilitated by specific _________________________. 12. ______________ proteins enable substances to diffuse through the membrane. A _________________ on each carrier protein fits a specific substance. As the substance fits into place, the carrier protein ___________________ . Part 3: Active Transport 13. ___________ transport is the movement of substances _____________ their concentration gradient. It requires the expenditure of cell _________________ in the form of ATP. 14. Describe how the gills of marine fish use active transport. 15. Describe endocytosis and name two types of molecules that move into the membrane through this process. 16. How is exocytosis different from endocytosis? 17. Explore Cell Transport and indicate the correct answer below for how each type of molecule travels through the membrane: Molecule Active or Passive Transport Amino Acid Bacterium Carbon Dioxide Neurotransmitter Potassium and Sodium Ions Sodium ions 18. What was your score? _____ / 15. Does it require a transport protein? Is there a specific name for this type of transport? Facilitated Diffusion, Endocytosis, Exocytosis