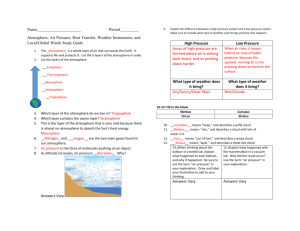
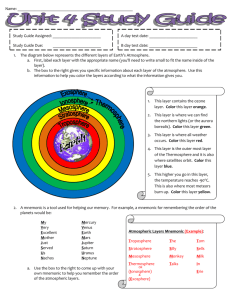
CH. 12 Cornell Notes
advertisement
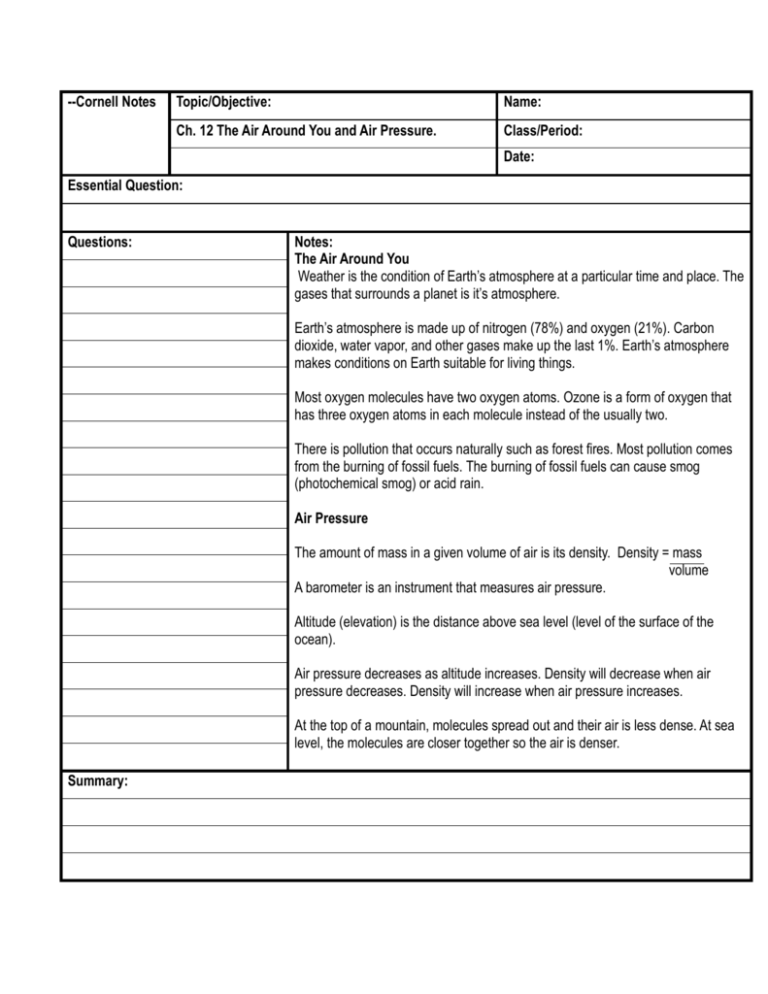
--Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: Name: Ch. 12 The Air Around You and Air Pressure. Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: Questions: Notes: The Air Around You Weather is the condition of Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time and place. The gases that surrounds a planet is it’s atmosphere. Earth’s atmosphere is made up of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases make up the last 1%. Earth’s atmosphere makes conditions on Earth suitable for living things. Most oxygen molecules have two oxygen atoms. Ozone is a form of oxygen that has three oxygen atoms in each molecule instead of the usually two. There is pollution that occurs naturally such as forest fires. Most pollution comes from the burning of fossil fuels. The burning of fossil fuels can cause smog (photochemical smog) or acid rain. Air Pressure The amount of mass in a given volume of air is its density. Density = mass volume A barometer is an instrument that measures air pressure. Altitude (elevation) is the distance above sea level (level of the surface of the ocean). Air pressure decreases as altitude increases. Density will decrease when air pressure decreases. Density will increase when air pressure increases. At the top of a mountain, molecules spread out and their air is less dense. At sea level, the molecules are closer together so the air is denser. Summary: Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: Ch12 sections 3-4 Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: Questions: Notes: Layers of the Atmosphere Scientists divide Earth’s atmosphere into four main layers: troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, and the thermosphere Earth’s weather occurs in the troposphere The stratosphere contains the ozone layer. The mesosphere protects Earth’s surface from the most meteoroids The outermost layer of Earth’s atmosphere is the thermosphere Energy in Earth’s Atmosphere Summary: Most energy from the sun travels to earth in the form of visible light Some sunlight is absorbed or reflected by the atmosphere before it can reach the surface When the Surface is heated, it radiates energy back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: Ch12 sections 5-6 Name: Class/Period: Date: Essential Question: Questions: Notes: Heat transfer in the Atmosphere Air temperature is usually measured with a thermometer Heat is transferred in three ways: radiation, conduction, and convection Radiation, conduction, and convection work together to heat the troposphere Energy in Earth’s Atmosphere Summary: Winds are caused by differences in air pressure Local winds are caused by the unequal heating of Earth’s surface within a small area Global winds are caused by the unequal heating of Earth’s surface over a large area Major global Wind belts are the trade winds, the polar easterlies, and the prevailing westerlies