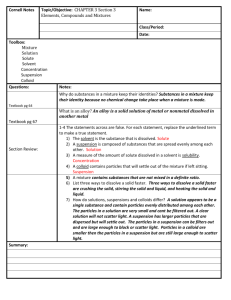
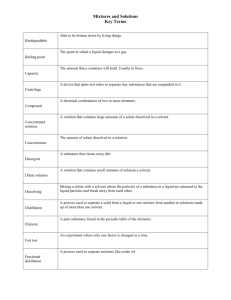
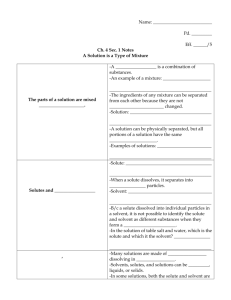
Science 7 Mixtures Unit Review: Questions that you should be able

Science 7 Mixtures Unit Review:
Questions that you should be able to answer:
1.
What are the states of matter
Liquid, Solid, Gas and plasma
2.
What are the four points of the particle theory a.
All matter is made up of tiny particles that are too small to see b.
These particles are always moving and vibrating. Solid particles move the least, and gas particles move the most c.
The particles of matter are all attracted or bonded to each other d.
The particles have spaces between them. Solid matter have small spaces than liquids and gases
3.
Explain mixing using the particle theory
However particles can also be attracted to other substances more than to themselves
4.
Why do some solutes dissolve in some solvents but not in others? Why is that that not all substances will dissolve in all substances?
In solutions the solute is more attracted to the water than it is to itself resulting in the solid separating
If the particles are more attracted to itself than it will remain a solid and remain a mixture
5.
Give examples of solutes that dissolve in certain solvents but that do not dissolve in different solvents.
Nail polish dissolves in nail polish remover but not in water
6.
What are some things that will you can try to dissolve substances faster?
Heat up the solvent, stir the mixture, break up the solute
7.
What are the two main ways that you can separate a mixture?
Sorting- physically separating/ picking a mixture, ex. picking out red m+m’s,
Filtering- using a filter/ sieve or other method to separate liquids or other mixtures that do not have distinct parts, ex filter out strawberry seeds to make jam
8.
Explain how you would separate water and dissolved ice tea crystals.
Evaporate the water and you’d be left with ice tea crystals
9.
Explain how you would separate out the marshmallows in lucky charms.
Pick them out (sorting)
10.
Explain how you would separate out metal nail in a patch of grass
Magnetic (think of separating sand and iron fillings)
11.
Know what WHMIS is and what the symbols in WHMIS mean. You may even have to give an example of where you might find that symbol.
Toxic, bioharzard and reactive are too hard to find common examples for
12.
Know the difference between a pure substance and mixture.
Pure substance has one property, Mixture is made up two or more substance each with their own distinctive properties
13.
Know the two types of mixtures: Mechanical and Solution and give an example of each.
Mechanical mixture: can see the components that make up the mixture ex omlete
Solution- mixture of liquids, still have distinct separate properties but they can not be seen separately
14.
Know the difference between solute, solvent and solution.
Solute is dissolved, Solvent does the dissolving, Solution is the resultant of a solute dissolving in a solvent
15.
Describe a heterogeneous and homogenous solution.
Heterogneous- not a uniform mixture and components can be easily separated (cereal and milk)
Homogenous- a uniform mixture where the components are mixed together and cannot be easily separated (air, glass)
16.
Students should know how to use a microscope and review how to make a proper drawing.
17.
Students should be able to describe how to use a microscope.
1.
Always start with the scanning objective . Odds are, you will be able to see something on this setting. Use the Coarse Knob to focus, image may be small at this magnification, but you won't be able to find it on the higher powers without this first step. Do not use stage clips, try moving the slide around until you find something.
2. Once you've focused on Scanning, switch to Low Power . Use the Coarse Knob to refocus.
Again, if you haven't focused on this level, you will not be able to move to the next level.
3. Now switch to High Power . (If you have a thick slide, or a slide without a cover, do NOT use the high power objective). At this point, ONLY use the Fine Adjustment Knob to focus specimens.
4. If the specimen is too light or too dark, try adjusting the diaphragm.
5. If you see a line in your viewing field, try twisting the eyepiece, the line should move. That's because its a pointer, and is useful for pointing out things to your lab partner or teacher.
18.
Students should know how to make a proper microscopic drawing.
Drawing Specimens
1. Use pencil - you can erase and shade areas
2. All drawings should include clear and proper labels (and be large enough to view details).
Drawings should be labeled with the specimen name and magnification.
3. Labels should be written on the outside of the circle. The circle indicates the viewing field as seen through the eyepiece, specimens should be drawn to scale - ie..if your specimen takes up the whole viewing field, make sure your drawing reflects that.
19.
Students should know the three main different types of sewage treatment.
Primary- filter out large particles of waste, grease and dirt- about 60%, water is too dirty to drink or swim in
Secondary- removes bacteria and offensive smells from the sludge and water. Filters out most of the waste (90%) and is clean enough to swim in but not to drink
Tertiary Uses chemicals and bacteria to filter out most of the waste and minerals to return the water to a more natural state. Tends to be used in centers that have a lot of people or do not have access to a good source of moving water
20.
Explain how detergents work? Name a natural cleaner that you could make and use every day.
Detergents work by attracting the dirt/ etc particles to them and because the detergent is water soluble, the dirt is simply washed away with the detergent
21.
Describe the differences in concentrations of solutions (ex. dilute, concentrated, saturated, super- saturated).
Dilute- not very much solute dissolved in the solvent (ex. minerals in drinking water)
Concentrated- more solutes dissolved in solvents (ex. concentrated juice before it is mixed with water)
Saturated- no more solute can be dissolved in the solvent
Super- Saturated (there is so much solute added that some of it remains undissolved at the bottom of the solvent (borax crystal ornaments)
22.
Why does society need to decrease the amount of non-biodegradable garbage that it produces?
It is harmful to the environment, hard and expensive to get rid of completely (ie burning it just converts it to the air, burying it causes it to seep into the soil, adding to wastewater means it needs to be filtered out)
23.
List one thing that you learned during this unit that you will remember.