File
advertisement
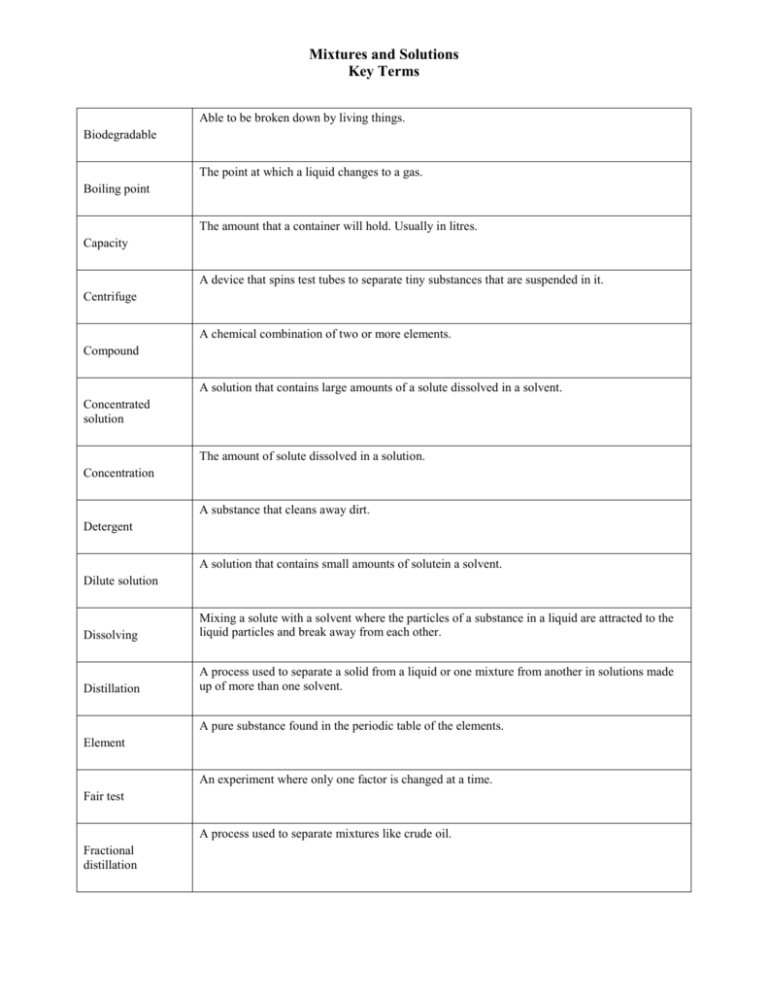
Mixtures and Solutions Key Terms Able to be broken down by living things. Biodegradable The point at which a liquid changes to a gas. Boiling point The amount that a container will hold. Usually in litres. Capacity A device that spins test tubes to separate tiny substances that are suspended in it. Centrifuge A chemical combination of two or more elements. Compound A solution that contains large amounts of a solute dissolved in a solvent. Concentrated solution The amount of solute dissolved in a solution. Concentration A substance that cleans away dirt. Detergent A solution that contains small amounts of solutein a solvent. Dilute solution Dissolving Mixing a solute with a solvent where the particles of a substance in a liquid are attracted to the liquid particles and break away from each other. Distillation A process used to separate a solid from a liquid or one mixture from another in solutions made up of more than one solvent. A pure substance found in the periodic table of the elements. Element An experiment where only one factor is changed at a time. Fair test A process used to separate mixtures like crude oil. Fractional distillation Mixtures and Solutions Key Terms Glass A manufactured material made by heating a mixture of substances that can include sand, carbonates and limestone. A long cylinder used to measure the volume of different types of liquids. Graduated cylinder Water that contains a lot of dissolved minerals. Hard water A mixture where you can see all the parts like soil. Heterogeneous mixture (mechanical mixture) A mixture where you cannot see the different parts. Homogeneous mixture (solution) The only factor that changes in an experiment that is a fair test. Independent variable Solute particles that do not bind with the solvent particles; not capable of dissolving. Insoluble The amount of matter in an object; usually measured in Grams. Mass Anything that occupies space (has mass and volume) Matter A mixture where you can see all the parts like soil. Mechanical mixture (heterogeneous mixture) A liquid at the lowest part of its curved surface. Meniscus Matter that is a combination of different substances like soil. Mixture Mixtures and Solutions Key Terms A method of determining if a liquid is a pure substance or a solution. Paper chromatography Particle Theory of Matter The theory that states that all matter is made up of tiny moving and vibrating particles that are attracted and bonded to each other and have spaces between them. A measure of how acidic or basic a substance is (0 – 14). pH Chemicals added to detergents to make more and better suds. Phosphates Primary treatment The first level of sewage treatment; removal of large chunks of waste; 60% of dirt and particles removed. Matter that has only one kind of substance in it, like table salt. Pure substance A solution in which no more solute can dissolve. Saturated solution Secondary treatment The second level of sewage treatment. Air and bacteria are used to break down sewage into less harmful materials. 90% of dirt and particles are removed. The waste that goes down the sink, drain and toilet. Sewage A type of detergent. Soap Water that has been treated with salt to remove minerals like calcium and magnesium. Soft water The maximum amount of solute that would dissolve in a particular amount of solvent. Solubility Able to dissolve. Soluble In a solution, the substance that dissolves. Solute Mixtures and Solutions Key Terms A mixture where you cannot see the different parts. Solution (homogeneous mixture) In a solution, the substance that does the dissolving. Solvent A very strong substance that is made of iron, carbon and small amounts of other substances. Steel Supersaturated solution A solution that is able to hold more solute than it normally be able to dissolve at a certain temperature. Surfactants Particles that attach themselves to dirt and oil particles and pull them into the water to be washed away. Tertiary treatment The third level of sewage treatment where all harmful things are removed using chemicals, filters and radiation. A solution where there is more room for the solute to dissolve. Unsaturated solution Volume The space that a three dimensional object takes up, usually measured in cubic meters and cubic centimeters.