Solutions & Colligative Properties Worksheet
advertisement

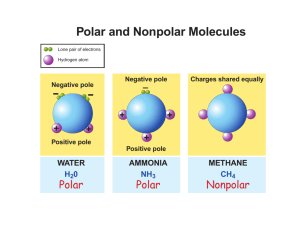
Solutions and Colligative Properties Name:________________________________________________________________Period:_________ Define the following terms: 1. Solution -- a homogenous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase 2. Solute -- a substance which is the portion of a solution that is dissolved. 3. Solvent -- a substance which is the portion of a solution that dissolves the solute; determines the phase of the solution. 4. Colloid -- a mixture whose particles are smaller than a suspension but larger than a solution and does not settle; the particles are suspended in a liquid, gas or solid. 5. Suspension -- A mixture whose particles are evenly dispersed in a gas or a liquid and which settle out over time. 6. Molarity -- the number of moles of a solute dissolved in a liter of solution. 7. Tyndall Effect -- a phenomenon where a beam of light is reflected off of the particles and visible to the naked eye 8. Concentration -- the measure of the amount of a particular substance in a given volume of solution. Fill in the Phase Chart Phase of Solute Solid Gas Gas Solid Liquid Phase of Solvent Solid Liquid Gas Liquid Liquid Phase of Solution Solid Liquid Gas Liquid liquid Example Alloy CO2 in Coke Air Sugar in Tea Rubbing alcohol 1. Which type of mixture has the smallest particles (circle): Colloids Suspensions Solutions 2. Which type of mixture has the largest particles (circle): Colloids Suspensions Solutions 3. Which type of mixture can have particles that will settle out of the solution? Solutions and Colligative Properties Colloids Suspensions Solutions 4. Which of the following are only one phase? Colloids Suspensions Solutions 5. What are the units of molarity (M)? mol/L 6. What are colligative properties? a property of a solution that is dependent upon the number of solute particles present and the nature of the solvent. 7. What do colligative properties affect? Boiling Point and Melting Point 8. When you add salt to water, will the boiling point increase or decrease? Increase 9. When you add salt to water, will the freezing point increase or decrease? Decrease 10. What does it mean “like dissolves like”? Like dissolves like refers to the ability of solutions to dissolve in one another. Polar molecules will dissolve in polar molecules and non-polar will dissolve in non-polar molecules. 11. Why doesn’t water mix with oil? Because water is polar and oil is non-polar Understand the Solubility Curve: What area of the curve represents unsaturated, supersaturated, or just saturated? The line represents the saturation point of a solid into 100g of water. The area above the line is where the solvent is super saturated. The area below the line is where the solvent is unsaturated. Solutions and Colligative Properties Problems: 1. What is the Molarity of a solution if there is 20.0g of H2SO4 in 250.0 mL of water? Solutions and Colligative Properties 2. What is the mass (g) of KBr in 25 mL of 0.85M solution of KBr? 3. How many moles of AgNO3 are needed to prepare 0.50L of a 4.0 M solution? 4. Calculate the mass of NaOH in 65.0 mL of 2.25 M solution. 5) M1V1=M2V2 (4M)(xL)=(1M)(0.500L) X = 0.125 L so, take 125 mL of the stock and bring it to a final volume of 500 mL