Ch. 4 4.1 Introduction to Atoms Review and Reinforce 1. Rutherford

Ch. 4
4.1 Introduction to Atoms
Review and Reinforce
1. Rutherford
2. Dalton
3. Bohr
4. Thomson
5. b
6. f
7. h
8. d
9. g
10. c
11. a
12. e
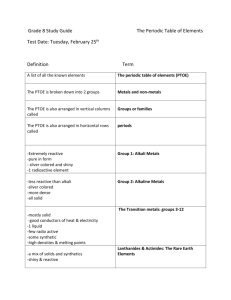
4.2 Organizing the Elements
Review and Reinforce
1. atomic number
2. chemical symbol
3. name
4. atomic mass
5. Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass.
6. Elements in a column have similar properties.
7. You can predict an element’s properties.
8. period
9. periodic table
10. group
11. chemical symbol
12. atomic mass
13. nuclear fusion
14. plasma
4.3 Metals
Review and Reinforce
1. Most metals are shiny, malleable, ductile, good conductors of heat and electricity, and solids at room temperature.
2. Sodium is in the family of alkali metals.
These metals are soft and shiny as pure elements. However, they are so reactive that they are never found uncombined in nature.
Calcium is in the family of alkaline earth metals.
Although they are less reactive than the alkali metals, these metals are also so reactive they are
never found uncombined in nature. They are fairly hard, silvery-white metals that are very good conductors of electricity.
3. A metal in Group 13 would be less reactive than a metal in Group 1. The reactivity of metals decreases as you move from left to right across the periodic table.
4. The lanthanides and actinides are in
Periods 6 and 7. They are grouped together beneath the rest of the periodic table to keep the table more compact.
5. corrosion
6. malleable
7. particle accelerator
8. conductivity
9. ductile
10. Reactivity
4.4 Nonmetals and Metalloids
Review and Reinforce
1. Metalloid, nitrogen family
2. Nonmetal, oxygen family
3. Metal, carbon family
4. Nonmetal, noble gas
5. Nonmetal, halogen
6. Metalloid, carbon family
7. The nonmetals are to the right of the metalloids. The metalloids are along a zigzag line between the metals and nonmetals.
8. Hydrogen; each atom has one proton and one electron.
9. c
10. f
11. a
12. b
13. e
14. d
4.5 Radioactive Elements
Review and Reinforce
1. gamma decay
2. alpha decay
3. beta decay
4. diagram 2
5. diagram 1
6. diagram 1
7. alpha particle
8. Gamma radiation
9. radioactivity
10. tracer
11. beta particle
12. radioactive decay