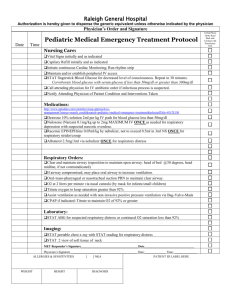
File
advertisement
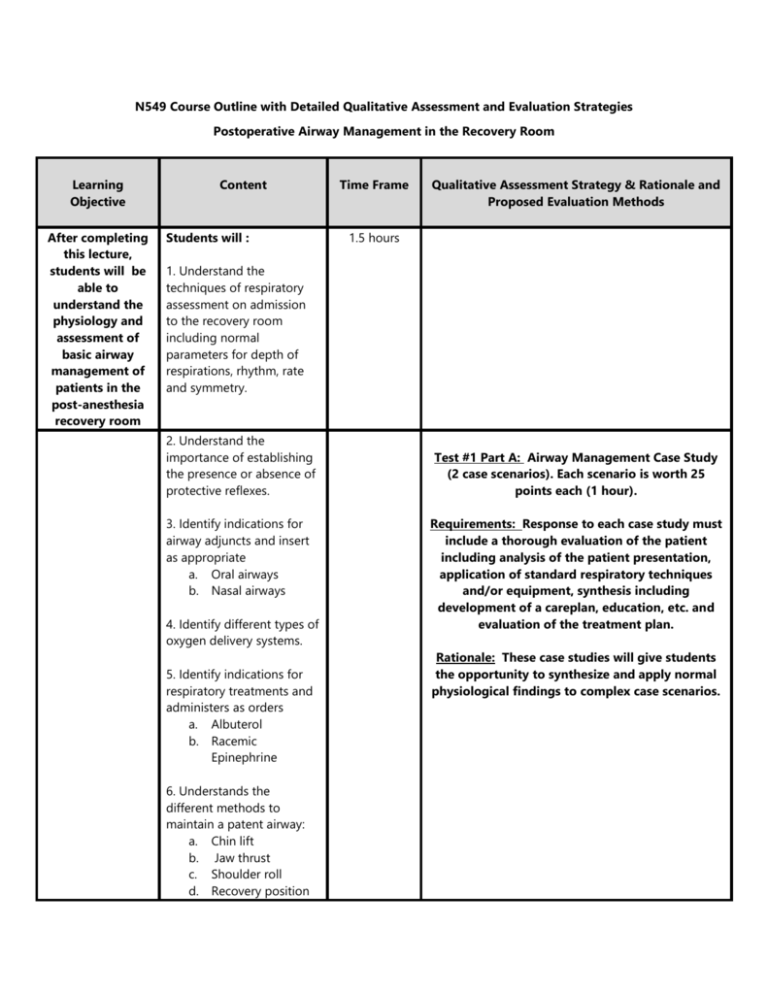
N549 Course Outline with Detailed Qualitative Assessment and Evaluation Strategies Postoperative Airway Management in the Recovery Room Learning Objective After completing this lecture, students will be able to understand the physiology and assessment of basic airway management of patients in the post-anesthesia recovery room Content Students will : Time Frame Qualitative Assessment Strategy & Rationale and Proposed Evaluation Methods 1.5 hours 1. Understand the techniques of respiratory assessment on admission to the recovery room including normal parameters for depth of respirations, rhythm, rate and symmetry. 2. Understand the importance of establishing the presence or absence of protective reflexes. 3. Identify indications for airway adjuncts and insert as appropriate a. Oral airways b. Nasal airways 4. Identify different types of oxygen delivery systems. 5. Identify indications for respiratory treatments and administers as orders a. Albuterol b. Racemic Epinephrine 6. Understands the different methods to maintain a patent airway: a. Chin lift b. Jaw thrust c. Shoulder roll d. Recovery position Test #1 Part A: Airway Management Case Study (2 case scenarios). Each scenario is worth 25 points each (1 hour). Requirements: Response to each case study must include a thorough evaluation of the patient including analysis of the patient presentation, application of standard respiratory techniques and/or equipment, synthesis including development of a careplan, education, etc. and evaluation of the treatment plan. Rationale: These case studies will give students the opportunity to synthesize and apply normal physiological findings to complex case scenarios. 7. Identify adventitious breath sounds and appropriate interventions for each: a. Rhonchi b. Crackles c. Wheezes d. Asymmetry or absence 8. Identify the work of breathing 9. Understand normal parameters for adequate oxygenation using pulse oximetry and identify scenarios when to increase oxygen delivery as appropriate. 10. State precautions for oxygen administration in patients with COPD. 11. Understand the mechanics of chest drainage systems 12. Understands and documents all pertinent information per standards of practice. 13. Identify signs and symptoms of respiratory complications associated with anesthesia: a. Bronchospasms b. Laryngospasms c. Pulmonary Edema d. Pulmonary Emboli e. Hypoxia f. Pneumothorax g. Subcutaneous air Learning Objective Content Time Frame After completing this lecture, students will understand the physiology and assessment of advance airway management in the post anesthesia recovery room. Students will : 1. Determine the effectiveness of ventilation 1.5 hours Qualitative Assessment Strategy & Rationale and Proposed Evaluation Methods 2. Understand the mechanics of bag-valvemask ventilation 3. Identify indications for endotracheal intubation. 4. List steps to assembling equipment and assist with intubation 5. Assess for proper endotracheal placement. a. Breath sounds b. Chest X-ray 6. List the steps for securing an endotracheal tube and assessing proper cuff inflation. 7. Describes the indications for short-term versus long term ventilation. 8. Describes modes of ventilation and their implications: a. Positive End Expiration Pressure (PEEP) b. Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) 9. Interpret arterial blood gases results: a. Pulmonary Acidosis b. Metabolic Acidosis c. Pulmonary Alkalosis Test #1 Part B: Advance Airway Management-5 Short Answer Essay Questions worth 10 points each (1 hour). Rationale: Critical thinking using the nursing process through student centered learning should result in “higher-order thinking.” According to McDonald (2014), Essay items give students the ability to compare, contrast, analyze, infer, and draw conclusions..” (p.187). Essays also give students the ability to theoretically apply evidence-based knowledge to real patient scenarios Examples Include: 1. Provide a short description of the different types of ventilator modes and indications for the modes. 2. Patient A is post-op a pneumonectomy and the physician has ordered a blood gas stat. The results show the following; ph 3.2, PCO2 78, PO2 90, Bicarbonate 18, saturation 84%. Interpret the test result (alkalosis vs. acidosis, metabolic versus pulmonary) and determine whether the patient is compensating, and, if so why. d. Metabolic Alkalosis e. Compensation 10. Identify indications for weaning and extubation of ventilated patients. 11. Identify extubation criteria for non-ventilated patients. 12. Identify equipment necessary for extubation. 13. Understands the post extubation steps of respiratory assessment: a. Respiratory effort b. Chest expansion c. Oxygen saturation d. Breath sounds e. Extubation 14. Understands and documents all pertinent information per standards of practice.