Covalent Bonding & Molecular Compounds
advertisement
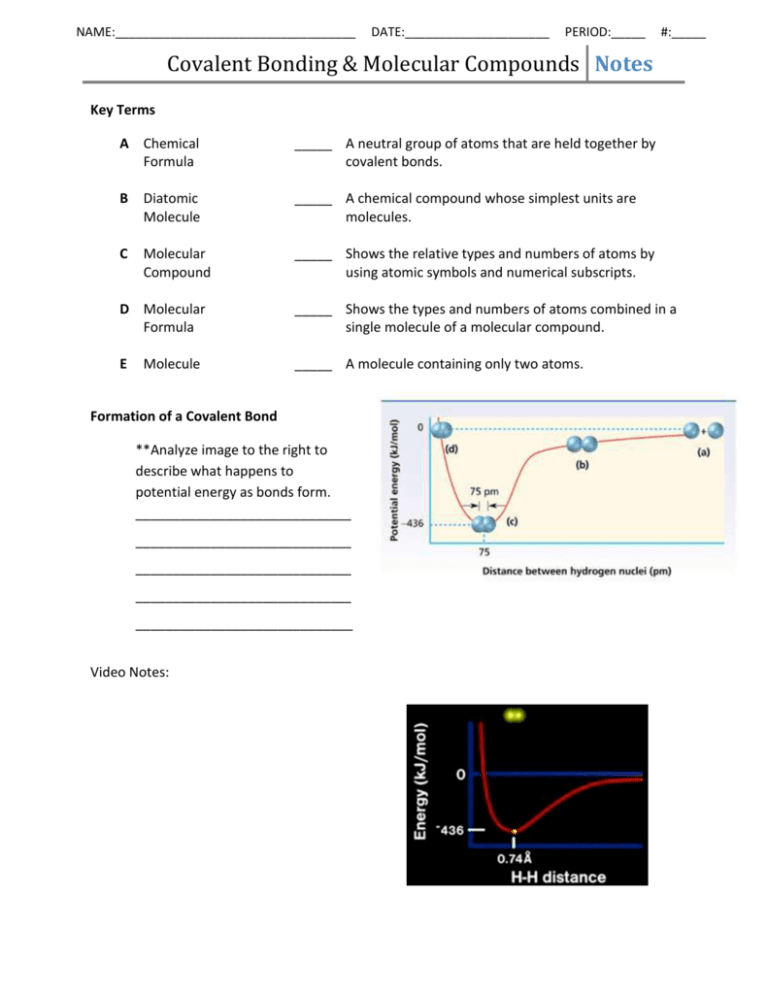
NAME:___________________________________ DATE:_____________________ PERIOD:_____ #:_____ Covalent Bonding & Molecular Compounds Notes Key Terms A Chemical Formula _____ A neutral group of atoms that are held together by covalent bonds. B Diatomic Molecule _____ A chemical compound whose simplest units are molecules. C Molecular Compound _____ Shows the relative types and numbers of atoms by using atomic symbols and numerical subscripts. D Molecular Formula _____ Shows the types and numbers of atoms combined in a single molecule of a molecular compound. E _____ A molecule containing only two atoms. Molecule Formation of a Covalent Bond **Analyze image to the right to describe what happens to potential energy as bonds form. _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ _____________________________ Video Notes: Covalent Bonding & Molecular Compounds Notes Characteristics of Covalent Bonds Bond length is ____________________________________________________________ Bond energy is ___________________________________________________________ **As bond length decreases, bond energy ________________. As bond length increases, bond energy ________________. Therefore, the relationship between bond length and bond energy is a(n) _______________ relationship. Octet Rule The octet rule states that chemical compounds _______________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Exceptions to the Octet Rule: Covalent Bonding & Molecular Compounds Notes Exceptions to the Octet Rule 1. Some elements are satisfied with fewer than 8 valence electrons: a. Hydrogen: __________________________________________ b. Beryllium: __________________________________________ c. Boron: _____________________________________________ 2. Some elements can be surrounded by more than eight electrons when they bind to highly electronegative atoms (F, O, Cl). Called an ______________________________. Lewis Structures A method for using electron-dot notation to represent molecules. Dots: __________________________________________________________ Dashes: ________________________________________________________ A shared pair of dots (electrons) is replaced with a __________. Steps for Drawing Lewis Structures 1. Determine the type and number of atoms in the molecule. Obtain the correct element cards from the bag. CH3I example: 2. Write the electron-dot notation for each type of atom and then determine the total number of valence electrons. Use different colored beads to represent the valence electrons around each type of atom. CH3I example: 3. Place atom with most open spaces (single electrons) in the middle. Arrange cards around the central atom. _____________ will always be in the center if present. _____________ & _____________ will never be centrally located. CH3I example: Covalent Bonding & Molecular Compounds Notes 4. Make sure each element (except hydrogen) is surrounded by 8 valence electrons. Replace bonding electron pairs (beads) with straw sticks. CH3I example: If not all atoms are surrounded by 8 valence electrons, move electron pairs to form double or triple bonds. __________ & __________ will never form double or triple bonds. 5. Check work by counting number of valence electrons. Should have same number of electrons as in step ____. CH3I example: Double Bond Example – CH2O Triple Bond Example – CO Single vs. Multiple Bonds Single bonds _____________________________________________________________ Multiple bonds ___________________________________________________________ Bond Type Double Triple Bond Length Bond Energy