Early Middle Ages: complete the chart by listing some of the effects
advertisement

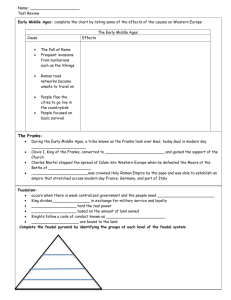
Early Middle Ages: complete the chart by listing some of the effects of the causes on Western Europe The Early Middle Ages Cause Effects The Fall of Rome Frequent invasions from barbarians such as the Vikings Roman road networks become unsafe to travel on People flee the cities to go live in the countryside People focused on basic survival The Franks: During the Early Middle Ages, a tribe known as the Franks took over Gaul, today Gaul is modern day France Clovis I, King of the Franks, converted to Christianity and gained the support of the Church Charles Martel stopped the spread of Islam into Western Europe when he defeated the Moors at the Battle of Tours Charlemagne was crowned Holy Roman Empire by the pope and was able to establish an empire that stretched across modern day France, Germany, and part of Italy Feudalism: occurs when there is weak centralized government and the people need protection King divides land in exchange for military service and loyalty Nobles hold the real power Power based on the amount of land owned Knights follow a code of conduct known as chivalry Serfs are peasants bound to the land Complete the feudal pyramid by identifying the groups at each level of the feudal system Feudalism (continued) Complete the feudalism obligations chart. Show the responsibilities that each group had towards the other group Lords Knights Serfs Manorial System: Economic system that developed along with Feudalism Primary economic activity was agriculture Manor was based on the concept of self sufficiency Role of the Church during the Middle Ages served as a unifying force in Western Europe after the fall of Rome Monks and Nuns in monasteries and abbots helped preserve Greek and Roman knowledge Popes had spiritual influence over followers and over time developed secular power Popes were able to influence political leaders by threatening to excommunicate rulers who did not follow the Church Popes and rulers often had conflicts over power in Europe o Pope Gregory tried to expand power of the church over rulers o Investiture Controversy developed over the right to appoint bishops Monarchs begin to Centralize Power: William of Normandy conquers England at the Battle of Hastings in 1066 o Gave lands to Norman supporters; determines who builds castles and where o Takes a census of called the Domesday Book in order to create an efficient tax system King John is forced to sign the Magna Carta o Limited the power of the monarch o King must obey the law o Magna Carta leads to the formation of the Parliament Crusades: Complete the chart below by identifying effects of the Crusades on Europe and the Middle East The Crusades Cause Effects Muslims controlled the Holy lands Byzantine was threatened by Seljuk Turks Pope Urban II calls for Crusades at the Council of Clermont Improvements in Farming: Complete the concept map by identifying three improvements to farming that helped lead to Improvements to Farming population growth in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. Commercial Revolution/ Growth of Cities and Towns Trade increased as a result of contact with Asia during the Crusades Italian city-states dominate trade in southern Europe; Flanders in the north o Examples: Genoa, Venice, Hanseatic League Trade Fairs and trading centers helped lead to the growth of cities and towns Formation of towns helped weaken feudalism Demand increased for currency rather than barter Banks develop to protect and invest people’s money Skilled workers and merchants form trade guilds to set prices and standards for quality Middle class begins to develop Art/Architecture/Literature/ Philosophy Architecture reflected the gothic style and use of flying buttress to construct much taller buildings and huge stained glass windows Canterbury Tales and Song of Roland are examples of Medieval literature Thomas Aquinas studied Greek philosophy; tried to use reason and logic to support Christian religious beliefs The Black Plague Complete the chart by identifying the effects of the Black Plague on Europe Characteristics Starts in China and spreads along trade routes towards the west Spread linked to trade with Asia and movement of Mongol invaders Spread by “fleas on rats♪♪♪” High fatality rate Unsanitary conditions and crowded cities helped spread the disease Black Plague Impact on Europe