Review Sheet for Chapter 3 Test: Acids, Bases and Solutions
advertisement

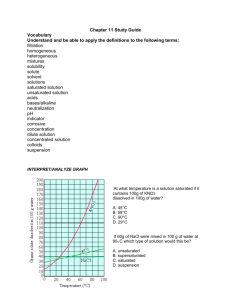
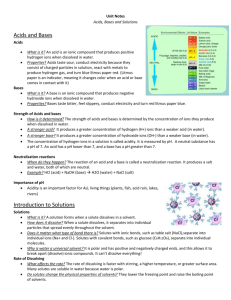
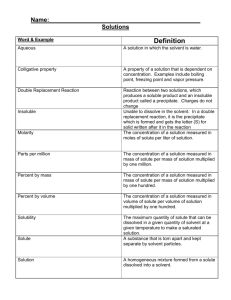
Name_________________________ Mr. Taylor-Waldman Review Sheet for Chapter 3 Test: Acids, Bases and Solutions – Test is Monday, May 4 Chapter 2, Section 2 – Describing Chemical Reactions Terms: chemical equation an easy way to show a chemical reaction using _________________ instead of words reactant the substances that you have at the beginning of a chemical reaction, on the left side product the substances produced in a chemical reaction, on the right synthesis a reaction where two reactants yield ______product. A + B C decomposition a reaction where one reactant yields two products. __________ replacement a reaction where two products split and reform two new products. AB + CD AC +BD Concepts: 1. Chemical equations must be “balanced” and have same number and type of atoms on both sides of the equation. Chapter 3, Section 1 – Understanding Solutions Terms solution: a well-mixed, _________________ mixture, made up of a solute and ______________, solute: the smaller part of a solution; it is what gets dissolved into a solvent (sugar in the soda) solvent: is the larger part of a solution; it dissolves the solute (water in the soda). suspension: a ________________ mixture in which the particles are large enough to be seen, and can be removed by ________________________ colloid: a ________________ mixture that contains small, undissolved particles that do not settle out; some colloids can also scatter light Concepts 1. Solutes lower the freezing point and _____________________ the boiling point of solvents. Chapter 3, Section 2 – Concentration and Solubility Terms concentration: a measurement comparing the amount of solute to the amount of solvent dilute solution: a mixture that has a ______________ ratio of solute to solvent concentrated solution: a mixture that has a ______________ ratio of solute to solvent saturated solution: a solution that has so much solute that ____________________________ unsaturated solution: a solution that can still dissolve more solute supersaturated solution: a solution with more dissolved solute than is predicted by its ________________________ at a given temperature solubility: the measure of how much solute can dissolve in a solvent ______________________ Concepts 1. Know how the factors of pressure, solvent type, and temperature affect solubility. 3. Know how to read solubility graphs, and how to make a statement of solubility. Chapter 3, Section 3 – Describing Acids and Bases Terms indicator: a compound (such as litmus paper of pH paper) that ____________________ when it comes into contact with an acid or a base corrosive: a property of acids; a substance’s ability to eat away metals Concepts 1. Know the properties of acids and bases, the chemical formulas of common acids and bases, their uses, and where they are found. Chapter 3, Section 4 – Acids and Bases in Solution Terms hydrogen ion (H+): a hydrogen atom that lost its electron, giving it a ________________________ hydroxide ion (OH-): a polyatomic ion made up of oxygen and hydrogen, carrying a - charge neutralization: a reaction between an acid and base yielding a solution that ________________________than the starting solutions Concepts 1. Acids produce ___________ and bases produce ___________ ions. 2. Know how the pH scale works, what it measures, and what determines whether and acid or base is strong or weak. 3. The pH scale measure the concentration of hydrogen ions 4. _______ paper is more accurate than _______ paper at describing acid/base strength. **Additional Concepts to Know** 1. Observing Chemical Change Lab 2. pH paper and Litmus paper homework Review Questions 1. Distinguish between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. 2. According to the principle of conservation of mass, what must be true in all chemical reactions? 3. What are two different examples of evidence that a chemical reaction has occurred? 4. Describe the part of our “Observing Chemical Reactions” Lab that can be represented by the following chemical equation: NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) → AgCl (s) + NaNO3 (aq)? What kind of substance was formed by this reaction? What is the name of this compound? Classify this type of reaction. 5. Using a balanced chemical equation, represent the chemical reaction of magnesium combustion that we observed in our lab. What type of chemical equation is this? 6. Which experiment in our “Observing Chemical Reactions” Lab that can be represented by this chemical equation: ___Al(s) + ___NaOH(aq) → ___H2(g) + ___Na3Al2O3(aq)? Which substance in this experiment is a strong base? 7. Balance the following equations, and classify each reaction as either synthesis, decomposition, single or double replacement. ____ Fe + ____ O2 → ____ Fe2O3 ____ P4 + ____ O2 → ____ P2O5 ____ NaCl + ____ F2 → ____ NaF + ____ Cl2 ____ C3H8 + ____ O2 → ____ CO2 + ____ H2O ____ NaHCO3 → ____ Na2CO3 + ____ H2O + ____ CO2 ____ Cu + ____ HNO3 → ____ Cu(NO3)2 + ____ NO + ____ H2O **extra challenging** 8. Give one example each of a solution, colloid and a suspension, and classify each as homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture. 9. How could you make a solution of lemonade (made with powder mix) more diluted? More concentrated? Increase its solubility? 10. What is an unsaturated solution? Saturated Solution? Supersaturated solution? 11. What property of solutions is calculated by comparing the amount of solute to the amount of solvent? 12. What two indicators can be used to test a substance’s pH? Which indicator is more precise? 13. How much potassium nitrate can be dissolved into 100 ml of water at 50°C? 14. Describe the solubility of hydrogen chloride at 20°C. 15. Can you dissolve 50 grams of sodium chloride into 100 ml of water at 30°C? How could you increase its solubility? 16. At what temperature can you dissolve exactly 105 grams of sodium nitrate into 100 ml of water? 17. Describe the difference between an acid and base in terms of the ions they form in water. 18. Describe the reaction of mixing a base with an acid. What is this called, and what products are formed? 19. How do solutes affect the freezing and boiling points of solvents? 20. What is an example of an acid, including chemical formula? Base, including chemical formula? 21. How would you describe a solution with a pH of 2? pH of 8? What pH is neutral?