Unit 5 Data Handling
advertisement

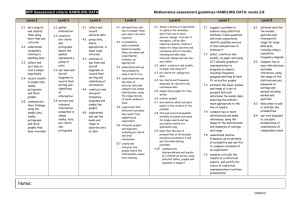
Unit 5: Data Handling Level 1 & Level 2 Level 3 (≈ Grade G/F) Level 4 (Grade E) Sort and classify objects using more than one criteria. Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Given a problem that can be addressed by statistical methods, suggest related questions to explore and decide what data to collect. Construct and interpret bar charts. Gather and record information in simple lists, tables and block graphs to communicate findings. Construct and interpret pictograms. Discuss and explain results. Construct and interpret simple line graphs. Extract and interpret information given in simple tables and lists. Interpret graphs and diagrams including pie charts and draw conclusions. Collect discrete data and record using a frequency table. Group data in equal class intervals and represent data in a frequency diagram. Interpret frequency diagrams. Understand and use the mode and range to describe sets of data. Understand and use the mean and median of discrete data. Compare two simple distributions using the range and one of the mode, median and mean. Unit 5: Data Handling Level 5 (≈ Grade D) Given a problem that can be addressed by statistical methods, suggest related questions to explore and decide what data to collect. Level 6 (≈ Grade C) Level 7 (≈ Grade B) Specify hypotheses and test them by designing and using appropriate methods that take account of variability and bias. Level 8 and E.P. (≈ Grade A/A*) Design a survey and data collection sheets to collect data. Determine appropriate sample size and degree of accuracy needed. Interpret graphs and diagrams including pie charts and draw conclusions. Collect and record discrete and continuous data choosing appropriate equal class intervals over a sensible range to create frequency tables. Interpret and construct cumulative frequency tables and diagrams using the upper boundary of the class interval. Construct and interpret pie charts and other frequency diagrams. Construct and interpret histograms. Construct and interpret composite bar-charts. Construct scatter diagrams and draw conclusions from them showing a basic understanding of correlation. Draw a line of best fit of a scatter diagram by inspection. Express general laws in symbolic form when finding formulae that approximately connect data. Determine the modal class, median class and estimate the mean and range of sets of grouped data, selecting the statistic most appropriate to their line of enquiry. Estimate the median and IQR and use these to compare distributions and make inferences. Construct on paper and using ICT a range of graphs and charts, identifying which are most useful in the context of a problem. Understand and use the mean and median of discrete data. Compare two simple distributions using the range and one of the mode, median and mean. Calculate the mean and mode from a frequency table. Use measures of average and range with associated frequency polygons to compare distributions and make inferences.