APP Assessment criteria HANDLING DATA Mathematics
advertisement

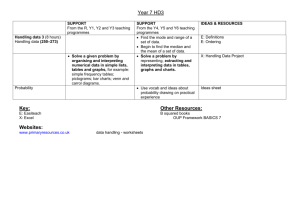
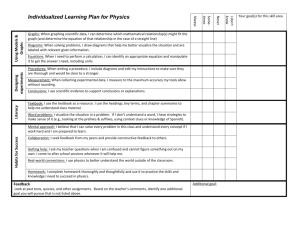
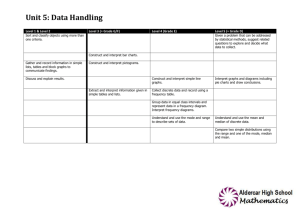
APP Assessment criteria HANDLING DATA Level 2 2.1 sort objects and classify them using more than one criterion 2.2 understand vocabulary relating to handling data 2.3 collect and sort data to test a simple hypothesis 2.4 record results in simple lists, tables, pictograms and block graphs 2.5 communicate their findings, using the simple lists, tables, pictograms and block graphs they have recorded Level 3 3.1 gather information 3.2 construct bar charts and pictograms, where the symbol represents a group of units 3.3 use Venn and Carroll diagrams to record their sorting and classifying of information 3.4 extract and interpret information presented in simple tables, lists, bar charts and pictograms Level 4 4.1 collect and record discrete data 4.2 group data, where appropriate, in equal class intervals 4.3 continue to use Venn and Carroll diagrams to record their sorting and classifying of information 4.4 construct and interpret frequency diagrams and simple line graphs 4.5 understand and use the mode and range to describe sets of data Mathematics assessment guidelines HANDLING DATA: levels 2-8 Level 5 Level 6 5.1 ask questions, plan how to answer them and collect the data required 6.1 design a survey or experiment to capture the necessary data from one or more sources; design, trial and, if necessary, refine data collection sheets; construct tables for large discrete and continuous sets of raw data, choosing suitable class intervals; design and use twoway tables 5.2 in probability, select methods based on equally likely outcomes and experimental evidence, as appropriate 5.3 understand and use the probability scale from 0 to 1y 5.4 understand and use the mean of discrete data and compare two simple distributions, using the range and one of mode, median or mean 5.5 understand that different outcomes may result from repeating an experiment 5.6 interpret graphs and diagrams, including pie charts, and draw conclusions 5.7 create and interpret line graphs where the intermediate values have meaning 6.2 select, construct and modify, on paper and using ICT: 6.3 pie charts for categorical data 6.4 bar charts and frequency diagrams for discrete and continuous data 6.5 simple time graphs for time series 6.6 scatter graphs 6.7 and identify which are most useful in the context of the problem 6.8 find and record all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for single events and two successive events in a systematic way 6.9 know that the sum of probabilities of all mutually exclusive outcomes is 1 and use this when solving problems 6.10 communicate interpretations and results of a statistical survey using selected tables, graphs and diagrams in support Level 7 7.1 suggest a problem to explore using statistical methods, frame questions and raise conjectures; identify possible sources of bias and plan how to minimise it 7.2 select, construct and modify, on paper and using ICT suitable graphical representation to progress an enquiry including frequency polygons and lines of best fit on scatter graphs 7.3 estimate the mean, median and range of a set of grouped data and determine the modal class, selecting the statistic most appropriate to the line of enquiry 7.4 compare two or more distributions and make inferences, using the shape of the distributions and measures of average and range Level 8 8.1 estimate and find the median, quartiles and interquartile range for large data sets, including using a cumulative frequency diagram 8.2 compare two or more distributions and make inferences, using the shape of the distributions and measures of average and spread including median and quartiles 8.3 know when to add or multiply two probabilities 8.4 use tree diagrams to calculate probabilities of combinations of independent event 7.5 understand relative frequency as an estimate of probability and use this to compare outcomes of an experiment 7.6 examine critically the results of a statistical enquiry, and justify the choice of statistical representation in written presentation Notes: 20090212