Portfolio
advertisement

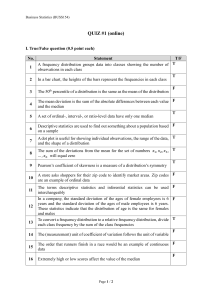
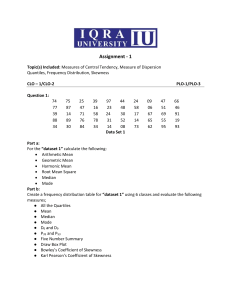
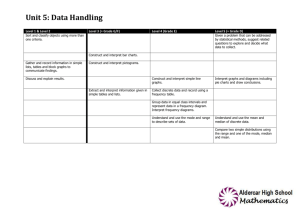
The portfolio is where you condense your notes to one page. Color code things and make it neat. Make the portfolio something that will be useful to you later. Don’t include formulas that are on the formula Sheet. You should include the interpretations. I would have a section for “How to do this on the Calculator.” There is plain white paper on my desk for you to use and markers and colored pencils on the side table. Get creative! I’m including the major topics that we have done so far. This is due on Wednesday, Oct. 15. Unit 2: Analyzing Data Read and make a frequency distribution table Read and make a relative frequency distribution table Categorical Data (Qualitative) – Pie Charts, Bar graphs, Segmented Bar Charts, Comparative Bar Charts Be able to find Marginal Distributions Be able to find Conditional Distributions Quantitative Data – Dotplots, Stemplots, histograms, Boxplots How to describe a quantitative Graph – Center, Shape, Spread Finding outliers Symmetry and skewness Mean and Median and skewness Finding measures of center – mean, median Finding measures of variability – range, standard deviation, variance, Interquartile range Which values are resistant Unit 3 – Modeling Distributions of Data Measures of position – Quartiles, Percentiles, Z-scores Using a cumulative relative frequency graph Transforming data & how the mean, median, and standard deviation are affected Using a density curve to find the area under the curve. Using the normal distribution to find probability Using the normal distribution to find a value when given the probability Using the empirical Rule Using a Normal probability plot Unit 4 – Describing Relationships Be able to draw and describe a scatter plot Be able to distinguish between an explanatory variable and a response variable. Know what the correlation coefficient is and how to interpret it. What affects the correlation coefficient Be able to find the LSRL Be able to predict using the LSRL Be able to find and interpret the slope Be able to find and interpret the y-intercept Know what extrapolation is Know what a residual is and how to find it Know what the standard deviation of the residuals is and how it is found Know how to find and interpret the coefficient of determination Know the what influential points are on a scatter plot Know what can tell you cause and effect and what does not Unit 1 – Experimental Design Know the difference between sample and population Know the types of sampling – SRS, Convenience, Voluntary, Stratified, Cluster, Systematic Know the types of bias – Selection, Non-response, Measurement/Response Know the difference between observational study and an experimental study Understanding confounding and lurking variables Be able to identify experimental units, factors, treatments, and response variables. Know the 4 basic principles of experimental design Know the three different designs – Completely randomized, Randomized Block, and Matched Pairs Know the difference between Blind and single blind Know what a placebo is and what a placebo effect is